Difference between revisions of "CheA"
(→References) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | ==Reviews== | |
| + | <pubmed> 20122866 </pubmed> | ||
| + | ==Original publications== | ||
<pubmed>1938941,12123464,17908686,8866475,12094812,10094672,11722727,14651647, 9657996,8157612,15175317 9721285 </pubmed> | <pubmed>1938941,12123464,17908686,8866475,12094812,10094672,11722727,14651647, 9657996,8157612,15175317 9721285 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 08:57, 5 February 2010
- Description: two-component sensor kinase, chemotactic signal modulator
| Gene name | cheA |
| Synonyms | cheN |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase |
| Function | chemotactic signal modulator |
| MW, pI | 74 kDa, 4.452 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2013 bp, 671 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | cheB, cheW |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 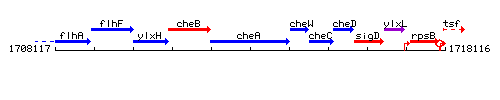
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16430
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: autophosphorylation, phosphorylation of CheY
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: autophosphorylation on a His residue
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P29072
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: flgB-flgC-fliE-fliF-fliG-fliH-fliI-fliJ-ylxF-fliK-ylxG-flgE-fliL-fliM-fliY-cheY-fliZ-fliP-fliQ-fliR-flhB-flhA-flhF-ylxH-cheB-cheA-cheW-cheC-cheD-sigD-swrB PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Gerald L Hazelbauer, Wing-Cheung Lai
Bacterial chemoreceptors: providing enhanced features to two-component signaling.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2010, 13(2);124-32
[PubMed:20122866]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications