Difference between revisions of "FtsH"
(→Basic information/ Evolution) |
(→Database entries) |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''Structure:''' | + | * '''Structure:''' [http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1LV7 1LV7] (from ''E. coli'', 64% identity) {{PubMed|12176385}} |
* '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P37476 P37476] | * '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P37476 P37476] | ||
Revision as of 14:25, 3 February 2010
- Description: ATP-dependent metalloprotease
| Gene name | ftsH |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATP-dependent metalloprotease |
| Function | cell division, sporulation initiation |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress | |
| MW, pI | 70 kDa, 5.841 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1911 bp, 637 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | hprT, coaX |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 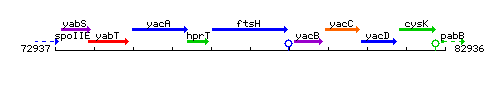
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00690
Phenotypes of a mutant
strongly reduced sporulation frequency
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: degrades Spo0E, resulting in reduced sporulation frequency in a ftsH mutant
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): YjoB
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot), membrane PubMed
Database entries
- UniProt: P37476
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: induced by heat shock (class III)
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information: the mRNA is very stable (half-life > 15 min) PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Ai Thi Thuy Le, Wolfgang Schumann
The Spo0E phosphatase of Bacillus subtilis is a substrate of the FtsH metalloprotease.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 4);1122-1132
[PubMed:19332814]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Matthias Kotschwar, Evita Harfst, Tanja Ohanjan, Wolfgang Schumann
Construction and analyses of mutant ftsH alleles of Bacillus subtilis involving the ATPase- and Zn-binding domains.
Curr Microbiol: 2004, 49(3);180-5
[PubMed:15386101]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Hambraeus, C von Wachenfeldt, L Hederstedt
Genome-wide survey of mRNA half-lives in Bacillus subtilis identifies extremely stable mRNAs.
Mol Genet Genomics: 2003, 269(5);706-14
[PubMed:12884008]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Stephan Zellmeier, Ulrich Zuber, Wolfgang Schumann, Thomas Wiegert
The absence of FtsH metalloprotease activity causes overexpression of the sigmaW-controlled pbpE gene, resulting in filamentous growth of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(3);973-82
[PubMed:12533473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R S Prajapati, T Ogura, S M Cutting
Structural and functional studies on an FtsH inhibitor from Bacillus subtilis.
Biochim Biophys Acta: 2000, 1475(3);353-9
[PubMed:10913836]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W Wehrl, M Niederweis, W Schumann
The FtsH protein accumulates at the septum of Bacillus subtilis during cell division and sporulation.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(13);3870-3
[PubMed:10851010]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W Schumann
FtsH--a single-chain charonin?
FEMS Microbiol Rev: 1999, 23(1);1-11
[PubMed:10077851]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, Y P Dailly, P Zuber, D P Clark
Characterization of anaerobic fermentative growth of Bacillus subtilis: identification of fermentation end products and genes required for growth.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(21);6749-55
[PubMed:9352926]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Elena Lysenko, Teru Ogura, Simon M Cutting
Characterization of the ftsH gene of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 1997, 143 ( Pt 3);971-978
[PubMed:9084181]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Deuerling, A Mogk, C Richter, M Purucker, W Schumann
The ftsH gene of Bacillus subtilis is involved in major cellular processes such as sporulation, stress adaptation and secretion.
Mol Microbiol: 1997, 23(5);921-33
[PubMed:9076729]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Deuerling, B Paeslack, W Schumann
The ftsH gene of Bacillus subtilis is transiently induced after osmotic and temperature upshift.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(14);4105-12
[PubMed:7608085]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)