Difference between revisions of "Sandbox"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' | + | * '''Description:''' glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Gene name''' | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Gene name''' glaube ich oder nicht |
| − | |'' | + | |''glmS'' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Synonyms''' || '' | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Synonyms''' || ''gcaA, ybxD '' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || yes [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12682299 PubMed] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || cell wall synthesis |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:# | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/subtipathways/search.php?enzyme=sandbox sandbox]''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| ''' | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 65 kDa, 4.796 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|''' | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || 1800 bp, 600 aa |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[glmM]]'', ''[[ybbU]]'' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image: | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Get the DNA and protein [http://srs.ebi.ac.uk/srsbin/cgi-bin/wgetz?-e+[EMBLCDS:CAB11954]+-newId sequences] <br/> (Barbe ''et al.'', 2009)''' |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:quintos.gif]] | ||
| + | <div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:test.gif]] | ||
<div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | <div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan="2" |'''[http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=glmS_200277_202079_1 Expression at a glance]'''   {{PubMed|22383849}}<br/>[[Image:glmS_expression.png|500px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| + | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[cell wall synthesis]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[biosynthesis of cell wall components]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[essential genes]]}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[glmS ribozyme]]}} | ||
=The gene= | =The gene= | ||
| Line 36: | Line 57: | ||
=== Basic information === | === Basic information === | ||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''Locus tag:''' BSU01780 |
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
| + | |||
| + | essential [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12682299 PubMed] | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [HELLO BSU00100] | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU00240&redirect=T"] | ||
| − | * '''DBTBS entry:''' | + | * '''DBTBS entry:''' no entry |
| − | * '''SubtiList entry:''' [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/genome.cgi?gene_detail+ | + | * '''SubtiList entry:''' [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/genome.cgi?gene_detail+BG10948] |
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| Line 52: | Line 77: | ||
=== Basic information/ Evolution === | === Basic information/ Evolution === | ||
| − | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' | + | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' L-glutamine + D-fructose 6-phosphate = L-glutamate + D-glucosamine 6-phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot) |
* '''Protein family:''' | * '''Protein family:''' | ||
| Line 63: | Line 88: | ||
* '''Domains:''' | * '''Domains:''' | ||
| − | |||
* '''Modification:''' | * '''Modification:''' | ||
| Line 69: | Line 93: | ||
* '''Cofactor(s):''' | * '''Cofactor(s):''' | ||
| − | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | + | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' |
| − | * '''Interactions:''' | + | * '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' |
| − | * '''Localization:''' | + | * '''[[Localization]]:''' |
| + | ** cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot) | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [HELLO BSU00100] | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU00240&redirect=T BSU00240] | ||
| − | * '''Structure:''' | + | * '''Structure:''' |
| + | **[http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=HIV2 HIV2] (from ''Bacillus subtilis'', 100% identity) {{PubMed|13454352}} | ||
| + | ** [http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2VF4 2VF4] (GlmS from ''E. coli'', 39% identity, 58% similarity) {{PubMed|18295797}} | ||
| + | ** the ribozyme: [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3g8s 3G8S], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3G9C 3G9C], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3g8t 3G8T], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3g95 3G95], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3g96 3G96] (all for the ribozyme from ''Bacillus anthracis''), [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2HO7 2HO7] (the ribozyme from ''Thermonanaerobacter tengcongensis'') | ||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P39754 P39754] |
| − | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu | + | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu:BSU01780] |
| + | |||
| + | * '''E.C. number:''' [http://www.expasy.org/enzyme/2.6.1.16 2.6.1.16] | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | + | :* subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=+17981983 PubMed] | |
=Expression and regulation= | =Expression and regulation= | ||
| − | * '''Operon:''' | + | * '''Operon:''' ''[[ybbP]]-[[ybbR]]-[[glmM]]-[[glmS]]'' |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=glmS_200277_202079_1 glmS] {{PubMed|22383849}} |
| − | * ''' | + | * '''Sigma factor:''' [[SigA]] {{PubMed|22211522}} |
| − | * ''' | + | * '''Regulation:''' |
| + | ** repressed by glucosamine, N-acetylglucosamine, N-propionylglucosamine or N-formylglucosamine {{PubMed|14343123}} | ||
| + | ** ''glmS'' is only expressed in the absence of glucosamine 6-phosphate ([[glmS]] [[ribozyme]]) | ||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' ''glmS'' [[ribozyme]]: glucosamine 6-phosphate binds the leader mRNA, and a [[riboswitch]] with [[ribozyme]] activity cleaves off the ''[[glmS]]'' section from the mRNA, resulting in stopp of transcript elongation |
| − | * '''Additional information:''' | + | * '''Additional information:''' |
| + | ** subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=+17981983 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** A [[ncRNA]] is predicted between ''[[glmM]]'' and ''[[glmS]]'' {{PubMed|20525796}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 2000 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 4000 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' | + | * '''Mutant:''' |
| − | * '''Expression vector:''' | + | * '''Expression vector:''' |
| − | + | ||
| − | * '''lacZ fusion:''' | + | * '''lacZ fusion:''' |
* '''GFP fusion:''' | * '''GFP fusion:''' | ||
| − | * '''Antibody:''' | + | * '''two-hybrid system:''' |
| + | |||
| + | * '''Antibody:''' | ||
=Labs working on this gene/protein= | =Labs working on this gene/protein= | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Wade Winkler]], University of Texas, USA, [http://www.utsouthwestern.edu/findfac/professional/0,,68018,00.html Homepage] |
=Your additional remarks= | =Your additional remarks= | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| + | ==Reviews== | ||
| + | <pubmed> 18279655 </pubmed> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==The ''glmS'' Ribozyme== | ||
| + | <pubmed>18079181 ,16484375, 16784238 ,15096624 , 16990543 ,17114942 ,16484375 , 15029187, 17283212 , 16298301, 19228039 21317896 21395279 </pubmed> | ||
| − | + | ==Other Original Publications== | |
| − | + | '''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|22211522}} | |
| − | + | <pubmed> 14343123 17981983 ,11160890, 18295797 20525796 </pubmed> | |
| − | + | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 13:22, 29 July 2014
- Description: glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase
| Gene name glaube ich oder nicht | glmS |
| Synonyms | gcaA, ybxD |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase |
| Function | cell wall synthesis |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: sandbox | |
| MW, pI | 65 kDa, 4.796 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1800 bp, 600 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | glmM, ybbU |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
| Genetic context File:Quintos.gif This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed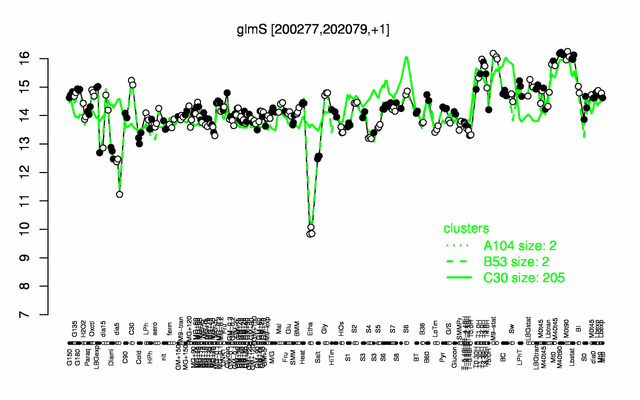
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, biosynthesis of cell wall components, essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU01780
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: [HELLO BSU00100]
- BsubCyc: "
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: L-glutamine + D-fructose 6-phosphate = L-glutamate + D-glucosamine 6-phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: [HELLO BSU00100]
- BsubCyc: BSU00240
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39754
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 2.6.1.16
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism: glmS ribozyme: glucosamine 6-phosphate binds the leader mRNA, and a riboswitch with ribozyme activity cleaves off the glmS section from the mRNA, resulting in stopp of transcript elongation
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- A ncRNA is predicted between glmM and glmS PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 2000 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 4000 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Wade Winkler, University of Texas, USA, Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
The glmS Ribozyme
Other Original Publications
Additional publications: PubMed