Difference between revisions of "Fur"
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>12029044, 19508286 , 12354229, 16672620, 19508285 , 18697947 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>18487332,12374814,14563870,18697947,10400588,11790741,16672620,12207695,9701813,12029044,,17725565,17012385,12950915,12029044, 19508286 , 12354229, 16672620, 19508285 , 18697947 </pubmed> |
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 22:50, 13 June 2009
- Description: transcription regulator of iron homoeostasis
| Gene name | fur |
| Synonyms | yqkL |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional repressor |
| Function | regulation of iron homoeostasis
and transcription of ferri-siderophore uptake genes |
| MW, pI | 17 kDa, 5.374 |
| Gene length, protein length | 447 bp, 149 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ripX, spoIIM |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 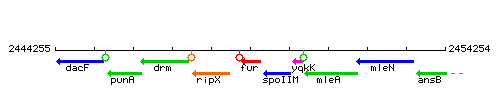
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU23520
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: Fur family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Genes controlled by Fur
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: P54574
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: fur
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
John Helmann, Cornell University, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
David P Giedroc
Hydrogen peroxide sensing in Bacillus subtilis: it is all about the (metallo)regulator.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 73(1);1-4
[PubMed:19508286]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
L Jacquamet, D A K Traoré, J-L Ferrer, O Proux, D Testemale, J-L Hazemann, E Nazarenko, A El Ghazouani, C Caux-Thang, V Duarte, J-M Latour
Structural characterization of the active form of PerR: insights into the metal-induced activation of PerR and Fur proteins for DNA binding.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 73(1);20-31
[PubMed:19508285]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ahmed Gaballa, Haike Antelmann, Claudio Aguilar, Sukhjit K Khakh, Kyung-Bok Song, Gregory T Smaldone, John D Helmann
The Bacillus subtilis iron-sparing response is mediated by a Fur-regulated small RNA and three small, basic proteins.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2008, 105(33);11927-32
[PubMed:18697947]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Falko Hochgräfe, Carmen Wolf, Stephan Fuchs, Manuel Liebeke, Michael Lalk, Susanne Engelmann, Michael Hecker
Nitric oxide stress induces different responses but mediates comparable protein thiol protection in Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(14);4997-5008
[PubMed:18487332]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ahmed Gaballa, John D Helmann
Substrate induction of siderophore transport in Bacillus subtilis mediated by a novel one-component regulator.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 66(1);164-73
[PubMed:17725565]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Marcus Miethke, Helga Westers, Evert-Jan Blom, Oscar P Kuipers, Mohamed A Marahiel
Iron starvation triggers the stringent response and induces amino acid biosynthesis for bacillibactin production in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(24);8655-7
[PubMed:17012385]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Juliane Ollinger, Kyung-Bok Song, Haike Antelmann, Michael Hecker, John D Helmann
Role of the Fur regulon in iron transport in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(10);3664-73
[PubMed:16672620]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Mayuree Fuangthong, John D Helmann
Recognition of DNA by three ferric uptake regulator (Fur) homologs in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(21);6348-57
[PubMed:14563870]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Emmanuel Guedon, Charles M Moore, Qiang Que, Tao Wang, Rick W Ye, John D Helmann
The global transcriptional response of Bacillus subtilis to manganese involves the MntR, Fur, TnrA and sigmaB regulons.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 49(6);1477-91
[PubMed:12950915]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Noel Baichoo, John D Helmann
Recognition of DNA by Fur: a reinterpretation of the Fur box consensus sequence.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(21);5826-32
[PubMed:12374814]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Noel Baichoo, Tao Wang, Rick Ye, John D Helmann
Global analysis of the Bacillus subtilis Fur regulon and the iron starvation stimulon.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 45(6);1613-29
[PubMed:12354229]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Min Cao, Tao Wang, Rick Ye, John D Helmann
Antibiotics that inhibit cell wall biosynthesis induce expression of the Bacillus subtilis sigma(W) and sigma(M) regulons.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 45(5);1267-76
[PubMed:12207695]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Mayuree Fuangthong, Andrew F Herbig, Nada Bsat, John D Helmann
Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis fur and perR genes by PerR: not all members of the PerR regulon are peroxide inducible.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(12);3276-86
[PubMed:12029044]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Tamara Hoffmann, Alexandra Schütz, Margot Brosius, Andrea Völker, Uwe Völker, Erhard Bremer
High-salinity-induced iron limitation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(3);718-27
[PubMed:11790741]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N Bsat, J D Helmann
Interaction of Bacillus subtilis Fur (ferric uptake repressor) with the dhb operator in vitro and in vivo.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(14);4299-307
[PubMed:10400588]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N Bsat, A Herbig, L Casillas-Martinez, P Setlow, J D Helmann
Bacillus subtilis contains multiple Fur homologues: identification of the iron uptake (Fur) and peroxide regulon (PerR) repressors.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 29(1);189-98
[PubMed:9701813]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)