Difference between revisions of "LicT"
(→Extended information on the protein: Added the domains and the phosphorylation sites) |
(→Extended information on the protein) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
* '''Modification:''' | * '''Modification:''' | ||
** phosphorylation at His-100 in PRD-1 by phosphorylated [[BglP]], inhibits LicT antitermination activity | ** phosphorylation at His-100 in PRD-1 by phosphorylated [[BglP]], inhibits LicT antitermination activity | ||
| − | ** phosphorylation at His-207 and/or His-269 in PRD-2 by His-P-[[ptsH|HPr]] | + | ** phosphorylation at His-207 and/or His-269 in PRD-2 by His-P-[[ptsH|HPr]], stimulates LicT antitermination activity |
* '''Cofactor(s):''' | * '''Cofactor(s):''' | ||
Revision as of 13:10, 3 June 2009
- Description: transcriptional antiterminator of the bglPH operon
| Gene name | licT |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional antiterminator (BglG family) |
| Function | required for substrate-dependent induction of bglPH |
| MW, pI | 32 kDa, 5.944 |
| Gene length, protein length | 831 bp, 277 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | bglS, yxiP |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 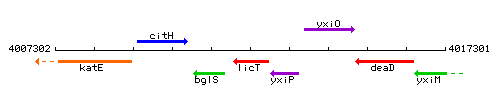
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU39080
Phenotypes of a mutant
no expression of the bglP-bglH operon
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: binding to the mRNAs of bglS and the bglP-bglH operon, causes transcription antitermination (in presence of salicin and absence of glucose)
- Protein family: transcriptional antiterminator bglG family (according to Swiss-Prot) BglG family of antiterminators
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Swiss prot entry: P39805
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Stephane Aymerich, Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, INRA Paris-Grignon, France
Josef Deutscher, Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, INRA Paris-Grignon, France
Michael Hecker, Greifswald, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Original description
K Schnetz, J Stülke, S Gertz, S Krüger, M Krieg, M Hecker, B Rak
LicT, a Bacillus subtilis transcriptional antiterminator protein of the BglG family.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(7);1971-9
[PubMed:8606172]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Control of LicT activity
Structural analysis of LicT
Hélène Déméné, Thierry Ducat, Karine De Guillen, Catherine Birck, Stéphane Aymerich, Michel Kochoyan, Nathalie Declerck
Structural mechanism of signal transduction between the RNA-binding domain and the phosphotransferase system regulation domain of the LicT antiterminator.
J Biol Chem: 2008, 283(45);30838-49
[PubMed:18682383]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Marc Graille, Cong-Zhao Zhou, Véronique Receveur-Bréchot, Bruno Collinet, Nathalie Declerck, Herman van Tilbeurgh
Activation of the LicT transcriptional antiterminator involves a domain swing/lock mechanism provoking massive structural changes.
J Biol Chem: 2005, 280(15);14780-9
[PubMed:15699035]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N Declerck, H Dutartre, V Receveur, V Dubois, C Royer, S Aymerich, H van Tilbeurgh
Dimer stabilization upon activation of the transcriptional antiterminator LicT.
J Mol Biol: 2001, 314(4);671-81
[PubMed:11733988]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H van Tilbeurgh, D Le Coq, N Declerck
Crystal structure of an activated form of the PTS regulation domain from the LicT transcriptional antiterminator.
EMBO J: 2001, 20(14);3789-99
[PubMed:11447120]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
LicT-RNA interaction
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed