Difference between revisions of "Aag"
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:yxlJ_context.gif]] | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:yxlJ_context.gif]] | ||
| + | <div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 18:39, 23 March 2009
- Description: general stress protein, similar to DNA-3-methyladenine glycosidase II
| Gene name | aag |
| Synonyms | yxlJ |
| Essential | no |
| Product | unknown |
| Function | survival of salt and ethanol stresses |
| MW, pI | 21 kDa, 6.117 |
| Gene length, protein length | 588 bp, 196 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yxzF, katX |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 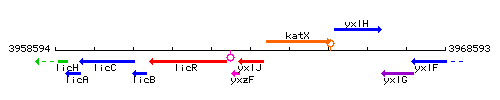
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates:
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: removes hypoxanthine, 3-alkylated purines, and 1,N6-ethenoadenine from DNA; hypoxanthine and 1,N6-ethenoadenine are the preferred substrates PubMed
- Protein family: AAG family of 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylases
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry:
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
- Aamodt et al. (2004) The Bacillus subtilis counterpart of the mammalian 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase has hypoxanthine and 1,N6-ethenoadenine as preferred substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 13601-13606-page. PubMed