Difference between revisions of "TasA"
(→Biological materials) |
(→Original publications) |
||
| Line 164: | Line 164: | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>23352144 23352134 23632024 23012477 21815947 21856853 18047568,16430695,16430696,10368135,18430133, 18647168 , 10464223,17720793,18957862 12107147 18763711, 20080671 10049401 23646920 24488317</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>23352144 23352134 23632024 23012477 21815947 21856853 18047568,16430695,16430696,10368135,18430133, 18647168 , 10464223,17720793,18957862 12107147 18763711, 20080671 10049401 23646920 24488317 25894589</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 08:47, 22 April 2015
- Description: major component of biofilm matrix, forms amyloid fibers
| Gene name | tasA |
| Synonyms | cotN, yqhF |
| Essential | no |
| Product | major component of biofilm matrix |
| Function | biofilm formation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: tasA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: TasA | |
| Regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: tasA | |
| MW, pI | 28 kDa, 5.442 |
| Gene length, protein length | 783 bp, 261 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | sinR, sipW |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 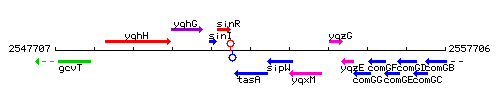
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed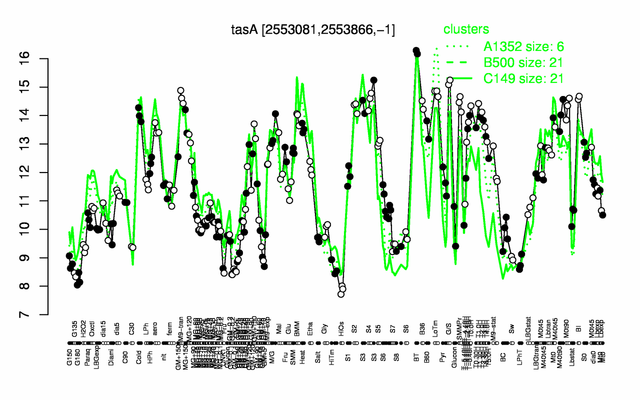
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
AbrB regulon, RemA regulon, SinR regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU24620
Phenotypes of a mutant
- altered cell death pattern in colonies PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU24620
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: forms amyloid fibers that bind cells together in the biofilm PubMed
- Protein family: peptidase M73 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU24620
- Structure:
- UniProt: P54507
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- induction by sequestration of SinR by SinI or SlrA PubMed or by SlrR PubMed
- the tapA-sipW-tasA operon is not expressed in a ymdB mutant PubMed
- the amount of the mRNA is substantially decreased upon depletion of RNase Y (this is likely due to the increased stability of the sinR mRNA) PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 199 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutants:
- 1S121 (tasA::spec), PubMed, available at BGSC
- GP1571 (cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP1663 (deletion of yqhG-sinI-sinR-tasA), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP1672 (deletion of sinR-tasA::cat) PubMed, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP1586 (cat) in the NCIB3610 background, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP1819 (aphA3), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Lynne S Cairns, Laura Hobley, Nicola R Stanley-Wall
Biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis: new insights into regulatory strategies and assembly mechanisms.
Mol Microbiol: 2014, 93(4);587-98
[PubMed:24988880]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Adam Driks
Tapping into the biofilm: insights into assembly and disassembly of a novel amyloid fibre in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 80(5);1133-6
[PubMed:21488983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Massimiliano Marvasi, Pieter T Visscher, Lilliam Casillas Martinez
Exopolymeric substances (EPS) from Bacillus subtilis: polymers and genes encoding their synthesis.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2010, 313(1);1-9
[PubMed:20735481]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yunrong Chai, Thomas Norman, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
An epigenetic switch governing daughter cell separation in Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 2010, 24(8);754-65
[PubMed:20351052]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
Jordi van Gestel, Hera Vlamakis, Roberto Kolter
From cell differentiation to cell collectives: Bacillus subtilis uses division of labor to migrate.
PLoS Biol: 2015, 13(4);e1002141
[PubMed:25894589]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Diego Romero, Hera Vlamakis, Richard Losick, Roberto Kolter
Functional analysis of the accessory protein TapA in Bacillus subtilis amyloid fiber assembly.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(8);1505-13
[PubMed:24488317]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jared T Winkelman, Anna C Bree, Ashley R Bate, Patrick Eichenberger, Richard L Gourse, Daniel B Kearns
RemA is a DNA-binding protein that activates biofilm matrix gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 88(5);984-97
[PubMed:23646920]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Liraz Chai, Diego Romero, Can Kayatekin, Barak Akabayov, Hera Vlamakis, Richard Losick, Roberto Kolter
Isolation, characterization, and aggregation of a structured bacterial matrix precursor.
J Biol Chem: 2013, 288(24);17559-68
[PubMed:23632024]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Diego Romero, Edgardo Sanabria-Valentín, Hera Vlamakis, Roberto Kolter
Biofilm inhibitors that target amyloid proteins.
Chem Biol: 2013, 20(1);102-10
[PubMed:23352144]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Emma K Andersson, Matthew Chapman
Small molecule disruption of B. subtilis biofilms by targeting the amyloid matrix.
Chem Biol: 2013, 20(1);5-7
[PubMed:23352134]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Munehiro Asally, Mark Kittisopikul, Pau Rué, Yingjie Du, Zhenxing Hu, Tolga Çağatay, Andra B Robinson, Hongbing Lu, Jordi Garcia-Ojalvo, Gürol M Süel
Localized cell death focuses mechanical forces during 3D patterning in a biofilm.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(46);18891-6
[PubMed:23012477]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Diethmaier, Nico Pietack, Katrin Gunka, Christoph Wrede, Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Christina Herzberg, Sebastian Hübner, Jörg Stülke
A novel factor controlling bistability in Bacillus subtilis: the YmdB protein affects flagellin expression and biofilm formation.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(21);5997-6007
[PubMed:21856853]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Marc Schaffer, Ulrike Mäder, Christine Diethmaier, Christina Herzberg, Jörg Stülke
RNA processing in Bacillus subtilis: identification of targets of the essential RNase Y.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 81(6);1459-73
[PubMed:21815947]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Diego Romero, Claudio Aguilar, Richard Losick, Roberto Kolter
Amyloid fibers provide structural integrity to Bacillus subtilis biofilms.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2010, 107(5);2230-4
[PubMed:20080671]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Birgit Voigt, Haike Antelmann, Dirk Albrecht, Armin Ehrenreich, Karl-Heinz Maurer, Stefan Evers, Gerhard Gottschalk, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Thomas Schweder, Michael Hecker
Cell physiology and protein secretion of Bacillus licheniformis compared to Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2009, 16(1-2);53-68
[PubMed:18957862]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kazuo Kobayashi
SlrR/SlrA controls the initiation of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 69(6);1399-410
[PubMed:18647168]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Frances Chu, Daniel B Kearns, Anna McLoon, Yunrong Chai, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
A novel regulatory protein governing biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 68(5);1117-27
[PubMed:18430133]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yunrong Chai, Frances Chu, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
Bistability and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 67(2);254-63
[PubMed:18047568]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Mark A Strauch, Benjamin G Bobay, John Cavanagh, Fude Yao, Angelo Wilson, Yoann Le Breton
Abh and AbrB control of Bacillus subtilis antimicrobial gene expression.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(21);7720-32
[PubMed:17720793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Steven S Branda, Frances Chu, Daniel B Kearns, Richard Losick, Roberto Kolter
A major protein component of the Bacillus subtilis biofilm matrix.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 59(4);1229-38
[PubMed:16430696]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Frances Chu, Daniel B Kearns, Steven S Branda, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
Targets of the master regulator of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 59(4);1216-28
[PubMed:16430695]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Knut Büttner, Rüdiger Bode, Michael Hecker
Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(15);4288-95
[PubMed:12107147]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A G Stöver, A Driks
Regulation of synthesis of the Bacillus subtilis transition-phase, spore-associated antibacterial protein TasA.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(17);5476-81
[PubMed:10464223]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Serrano, R Zilhão, E Ricca, A J Ozin, C P Moran, A O Henriques
A Bacillus subtilis secreted protein with a role in endospore coat assembly and function.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(12);3632-43
[PubMed:10368135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A G Stöver, A Driks
Secretion, localization, and antibacterial activity of TasA, a Bacillus subtilis spore-associated protein.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(5);1664-72
[PubMed:10049401]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)