Difference between revisions of "GltC"
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
* '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | * '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | ||
** active as dimer | ** active as dimer | ||
| − | ** GltC-[[RocG]], This interaction takes place in the presence of glutamate. It prevents the transcription activation of the ''[[gltA]]-[[gltB]]'' operon. Note that [[RocG]] expression is strongly regulated by carbon and nitrogen sources, respectively | + | ** [[GltC]]-[[RocG]], This interaction takes place in the presence of glutamate. It prevents the transcription activation of the ''[[gltA]]-[[gltB]]'' operon. Note that [[RocG]] expression is strongly regulated by carbon and nitrogen sources, respectively {{PubMed|17608797}} |
| + | ** [[GltC]]-[[GudB]] {{PubMed|25711804}} | ||
* '''[[Localization]]:''' | * '''[[Localization]]:''' | ||
| Line 130: | Line 131: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' GP344 (erm), GP738 (spc) (available in [[Stülke]] lab) | + | * '''Mutant:''' GP344 (erm), GP738 (spc) (available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab) |
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
| − | ** for expression, purification in ''E. coli'' with N-terminal His-tag, in [[pWH844]]: pGP903, available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | ** for expression, purification in ''E. coli'' with N-terminal His-tag, in [[pWH844]]: pGP903, available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
| − | ** for expression, purification in ''E. coli'' with C-terminal Strep-tag, in pET3C: pGP951, available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | ** for expression, purification in ''E. coli'' with C-terminal Strep-tag, in pET3C: pGP951, available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
* '''lacZ fusion:''' | * '''lacZ fusion:''' | ||
| Line 140: | Line 141: | ||
* '''GFP fusion:''' | * '''GFP fusion:''' | ||
| − | * '''two-hybrid system:''' ''B. pertussis'' adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system ([[BACTH]]), available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | * '''two-hybrid system:''' ''B. pertussis'' adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system ([[BACTH]]), available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
| − | * '''Antibody:''' available in Stülke lab | + | * '''Antibody:''' available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
=Labs working on this gene/protein= | =Labs working on this gene/protein= | ||
| Line 161: | Line 162: | ||
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>7559360 15150225 2548995 17183217 17608797 17134717 14523131, 20630473</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>7559360 15150225 2548995 17183217 17608797 17134717 14523131, 20630473 25711804</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 13:00, 3 March 2015
- Description: Transcriptional activator of the gltA-gltB operon. Activates expression of the operon in the absence of arginine.
| Gene name | gltC |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | No |
| Product | transcriptional regulator (LysR family) |
| Function | positive regulation of the glutamate synthase operon (gltAB) |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: gltC | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: GltC | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: gltC | |
| MW, pI | 33.9 kDa, 5.62 |
| Gene length, protein length | 900 bp, 300 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | gltA, proJ |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 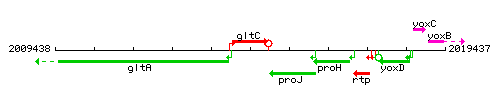
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, glutamate metabolism, transcription factors and their control
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The GltC regulon:
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU18460
Phenotypes of a mutant
gltC mutants are auxotrophic for glutamate.
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU18460
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry:[2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Protein family: LysR family PubMed
- Paralogous protein(s): none, but there are 19 members of the LysR family in B. subtilis
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: DNA-binding helix-turn-helix motif: AA 18 ... 37
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: 2-oxoglutarate stimulates transcription activation, glutamate inhibits transcription activation PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU18460
- Structure:
- UniProt: P20668
- KEGG entry: [3]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: autoregulation by GltC PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism: autorepression PubMed
- Database entries: DBTBS
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 43 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP344 (erm), GP738 (spc) (available in Jörg Stülke's lab)
- Expression vector:
- for expression, purification in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP903, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for expression, purification in E. coli with C-terminal Strep-tag, in pET3C: pGP951, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody: available in Jörg Stülke's lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Fabian Commichau University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications