Difference between revisions of "PycA"
(→Biological materials) |
|||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' GP793 (cat), available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab | + | * '''Mutant:''' |
| + | ** GP793 (cat), available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab | ||
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
Revision as of 13:40, 8 December 2014
- Description: pyruvate carboxylase
| Gene name | pycA |
| Synonyms | ylaP |
| Essential | no |
| Product | pyruvate carboxylase |
| Function | replenishment of the oxaloacetate pool |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: pycA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: pycA | |
| MW, pI | 127 kDa, 5.407 |
| Gene length, protein length | 3444 bp, 1148 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ftsW, ctaA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 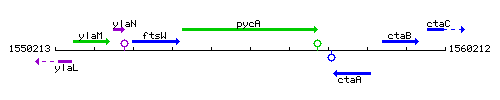
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
carbon core metabolism, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU14860
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14860
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactors: biotin
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14860
- Structure: 3BG5 (S. aureus)
- UniProt: Q9KWU4
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 6.4.1.1
Additional information
PycA binds to StrepTactin, and may be co-purified when purifying Strep-tagged proteins by SPINE.
PycA is subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- subject to positive stringent control upon lysine starvation PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- stringent response: due to presence of adenines at +1 and +2 positions of the transcript PubMed
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 2222 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 6831 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1602 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 907 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2037 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP793 (cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Leigh G Monahan, Isabella V Hajduk, Sinead P Blaber, Ian G Charles, Elizabeth J Harry
Coordinating bacterial cell division with nutrient availability: a role for glycolysis.
mBio: 2014, 5(3);e00935-14
[PubMed:24825009]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Shigeo Tojo, Kanako Kumamoto, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Heavy involvement of stringent transcription control depending on the adenine or guanine species of the transcription initiation site in glucose and pyruvate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(6);1573-85
[PubMed:20081037]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)