Difference between revisions of "Efp"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 146: | Line 146: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>15066026,17981983 23239624 23239623</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>15066026,17981983 23239624 23239623 25310979 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 15:32, 20 October 2014
- Description: elongation factor P, important for the translation of proteins containing three or more consecutive proline residues
| Gene name | efp |
| Synonyms | yqhU, yqgF |
| Essential | no |
| Product | elongation factor P |
| Function | translation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: efp | |
| MW, pI | 20 kDa, 4.845 |
| Gene length, protein length | 555 bp, 185 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yqhV, papA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed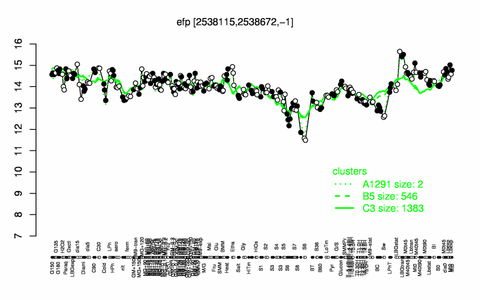
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
translation, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
Efp-dependent proteins
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU24450
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU24450
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: transpeptidase family (according to Swiss-Prot) elongation factor P family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot), cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU24450
- Structure: 1YBY (Efp from Clostridium thermocellum)
- UniProt: P49778
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 649 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2275 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 5117 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1779 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1876 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Agata L Starosta, Jürgen Lassak, Lauri Peil, Gemma C Atkinson, Christopher J Woolstenhulme, Kai Virumäe, Allen Buskirk, Tanel Tenson, Jaanus Remme, Kirsten Jung, Daniel N Wilson
A conserved proline triplet in Val-tRNA synthetase and the origin of elongation factor P.
Cell Rep: 2014, 9(2);476-83
[PubMed:25310979]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lili K Doerfel, Ingo Wohlgemuth, Christina Kothe, Frank Peske, Henning Urlaub, Marina V Rodnina
EF-P is essential for rapid synthesis of proteins containing consecutive proline residues.
Science: 2013, 339(6115);85-8
[PubMed:23239624]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Susanne Ude, Jürgen Lassak, Agata L Starosta, Tobias Kraxenberger, Daniel N Wilson, Kirsten Jung
Translation elongation factor EF-P alleviates ribosome stalling at polyproline stretches.
Science: 2013, 339(6115);82-5
[PubMed:23239623]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ulf Gerth, Holger Kock, Ilja Kusters, Stephan Michalik, Robert L Switzer, Michael Hecker
Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(1);321-31
[PubMed:17981983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Daniel B Kearns, Frances Chu, Rivka Rudner, Richard Losick
Genes governing swarming in Bacillus subtilis and evidence for a phase variation mechanism controlling surface motility.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 52(2);357-69
[PubMed:15066026]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)