Difference between revisions of "SipS"
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
| + | ** a ''[[sipS]] [[sipT]]'' double mutant is not viable {{PubMed|9694797}} | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| Line 64: | Line 65: | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 15:37, 4 October 2014
- Description: signal peptidase I
| Gene name | sipS |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | signal peptidase I |
| Function | protein secretion
(modulation of the capacity and specificity for protein secretion) |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: sipS
(modulation of the capacity and specificity for protein secretion) | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: SipS | |
| MW, pI | 20 kDa, 9.718 |
| Gene length, protein length | 552 bp, 184 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ypuD, ypzC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 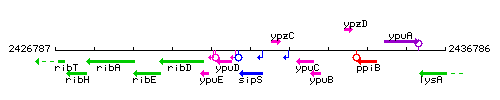
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
| Expression at a glance PubMed 500px | |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein secretion, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU23310
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU23310
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Cleavage of hydrophobic, N-terminal signal or leader sequences from secreted and periplasmic proteins (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: peptidase S26 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: membrane
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU23310
- Structure:
- UniProt: P28628
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: sipS PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jan Maarten van Dijl, Groningen, Netherlands
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Ross E Dalbey, Peng Wang, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Membrane proteases in the bacterial protein secretion and quality control pathway.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2012, 76(2);311-30
[PubMed:22688815]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
A Bolhuis, H Tjalsma, K Stephenson, C R Harwood, G Venema, S Bron, J M van Dijl
Different mechanisms for thermal inactivation of Bacillus subtilis signal peptidase mutants.
J Biol Chem: 1999, 274(22);15865-8
[PubMed:10336490]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Tjalsma, A Bolhuis, M L van Roosmalen, T Wiegert, W Schumann, C P Broekhuizen, W J Quax, G Venema, S Bron, J M van Dijl
Functional analysis of the secretory precursor processing machinery of Bacillus subtilis: identification of a eubacterial homolog of archaeal and eukaryotic signal peptidases.
Genes Dev: 1998, 12(15);2318-31
[PubMed:9694797]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Tjalsma, M A Noback, S Bron, G Venema, K Yamane, J M van Dijl
Bacillus subtilis contains four closely related type I signal peptidases with overlapping substrate specificities. Constitutive and temporally controlled expression of different sip genes.
J Biol Chem: 1997, 272(41);25983-92
[PubMed:9325333]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Bolhuis, A Sorokin, V Azevedo, S D Ehrlich, P G Braun, A de Jong, G Venema, S Bron, J M van Dijl
Bacillus subtilis can modulate its capacity and specificity for protein secretion through temporally controlled expression of the sipS gene for signal peptidase I.
Mol Microbiol: 1996, 22(4);605-18
[PubMed:8951809]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)