Difference between revisions of "MotA"
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
* '''Protein family:''' motA family (according to Swiss-Prot) | * '''Protein family:''' motA family (according to Swiss-Prot) | ||
| − | * '''Paralogous protein(s):''' | + | * '''Paralogous protein(s):''' [[MotP]] |
=== Extended information on the protein === | === Extended information on the protein === | ||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed> 6313226 21821766 22821967 24296669 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 6313226 21821766 22821967 24296669 24771657 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 08:17, 5 May 2014
| Gene name | motA |
| Synonyms | mot |
| Essential | no |
| Product | motility protein (flagellar motor rotation) |
| Function | motility and chemotaxis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: motA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: MotA | |
| MW, pI | 29 kDa, 5.01 |
| Gene length, protein length | 810 bp, 270 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | motB, clpE |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 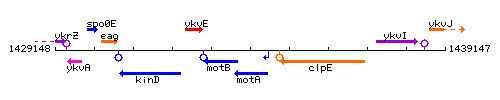
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed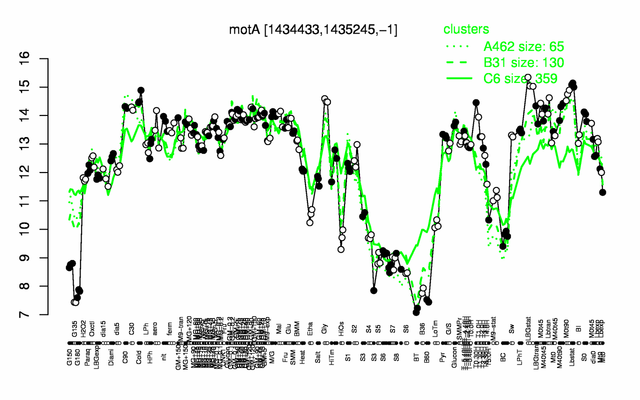
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
motility and chemotaxis, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13690
Phenotypes of a mutant
- loss of swimming and swarming motility PubMed
- mucoid phenotype due to the DegU-P activated overexpression of the capB-capC-capA-capE operon and resulting overproduction of poly-gamma-glutamate PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU13690
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
- A mutation was found in this gene after evolution under relaxed selection for sporulation PubMed
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: motA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): MotP
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU13690
- Structure:
- UniProt: P28611
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor: SigD PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Yuka Takahashi, Masahiro Ito
Mutational analysis of charged residues in the cytoplasmic loops of MotA and MotP in the Bacillus subtilis flagellar motor.
J Biochem: 2014, 156(4);211-20
[PubMed:24771657]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jia Mun Chan, Sarah B Guttenplan, Daniel B Kearns
Defects in the flagellar motor increase synthesis of poly-γ-glutamate in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(4);740-53
[PubMed:24296669]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yun Chen, Yunrong Chai, Jian-hua Guo, Richard Losick
Evidence for cyclic Di-GMP-mediated signaling in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(18);5080-90
[PubMed:22821967]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christopher T Brown, Laura K Fishwick, Binna M Chokshi, Marissa A Cuff, Jay M Jackson, Travis Oglesby, Alison T Rioux, Enrique Rodriguez, Gregory S Stupp, Austin H Trupp, James S Woollcombe-Clarke, Tracy N Wright, William J Zaragoza, Jennifer C Drew, Eric W Triplett, Wayne L Nicholson
Whole-genome sequencing and phenotypic analysis of Bacillus subtilis mutants following evolution under conditions of relaxed selection for sporulation.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2011, 77(19);6867-77
[PubMed:21821766]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
M Z Gilman, M J Chamberlin
Developmental and genetic regulation of Bacillus subtilis genes transcribed by sigma 28-RNA polymerase.
Cell: 1983, 35(1);285-93
[PubMed:6313226]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)