Difference between revisions of "PtsI"
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
** belongs to the 100 [[most abundant proteins]] {{PubMed|15378759}} | ** belongs to the 100 [[most abundant proteins]] {{PubMed|15378759}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3157 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 4976 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
Revision as of 09:31, 17 April 2014
- Description: Enzyme I, general (non sugar-specific) component of the PTS. Enzyme I transfers the phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to the phosphoryl carrier protein (HPr)
| Gene name | ptsI |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | phosphotransferase system (PTS) enzyme I |
| Function | PTS-dependent sugar transport |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ptsI | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: PtsI | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: ptsI | |
| MW, pI | 62,9 kDa, 4.59 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1710 bp, 570 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | ptsH, splA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 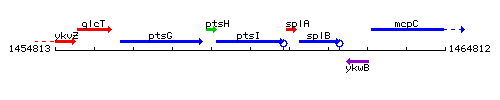
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed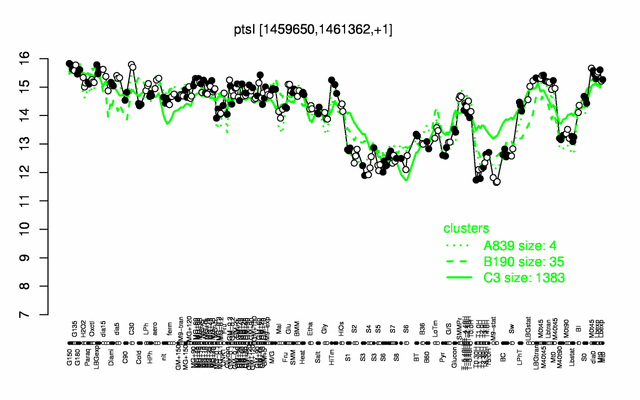
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
phosphotransferase systems, phosphoproteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
GlcT regulon, stringent response
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13910
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU13910
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Phosphoenolpyruvate + protein L-histidine = pyruvate + protein N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine (according to Swiss-Prot) PEP-dependent autophosphorylation on His-189, transfer of the phosphoryl group to HPr (His-15)
- Protein family: PEP-utilizing enzyme family (according to Swiss-Prot) PEP-utilizing enzyme family
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- HPr binding site (N-Terminal Domain)
- pyruvate binding site (C-Terminal Domain)
- pyrophosphate/phosphate carrier histidine (central Domain)
- Modification:
- transient autophosphorylation on His-189
- in vivo also phosphorylated on Ser-34 or Ser-36 PubMed
- Cofactors: Magnesium
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm, even distribution PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU13910
- UniProt: P08838
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.3.9 2.7.3.9]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- ptsG: transcriptional antitermination via the GlcT-dependent RNA switch PubMed
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3157 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 4976 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: available in Jörg Stülke's lab:
- Expression vector:
- pAG3 (His-tag) PubMed, available in Galinier lab
- for expression, purification in E. coli (His-tag), in pWH844: pGP813 available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- YFP fusion: B. subtilis GP1276 ptsI-yfp ermC, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Josef Deutscher, Paris-Grignon, France
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Sutharsan Govindarajan, Yair Elisha, Keren Nevo-Dinur, Orna Amster-Choder
The general phosphotransferase system proteins localize to sites of strong negative curvature in bacterial cells.
mBio: 2013, 4(5);e00443-13
[PubMed:24129255]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Fabian M Rothe, Christoph Wrede, Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Boris Görke, Jörg Stülke
Dynamic localization of a transcription factor in Bacillus subtilis: the LicT antiterminator relocalizes in response to inducer availability.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(10);2146-54
[PubMed:23475962]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shigeo Tojo, Kanako Kumamoto, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Heavy involvement of stringent transcription control depending on the adenine or guanine species of the transcription initiation site in glucose and pyruvate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(6);1573-85
[PubMed:20081037]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Anselm E Oberholzer, Philipp Schneider, Christian Siebold, Ulrich Baumann, Bernhard Erni
Crystal structure of enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate sugar phosphotransferase system in the dephosphorylated state.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(48);33169-76
[PubMed:19801641]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L F Garrity, S L Schiel, R Merrill, J Reizer, M H Saier, G W Ordal
Unique regulation of carbohydrate chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis by the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system and the methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein McpC.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(17);4475-80
[PubMed:9721285]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)