Difference between revisions of "CheY"
(→Database entries) |
|||
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
* '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU16330&redirect=T BSU16330] | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU16330&redirect=T BSU16330] | ||
| − | * '''Structure:''' | + | * '''Structure:''' [http://pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1tmy 1TMY] ([[CheY]] from ''Thermotoga maritima'') |
* '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P24072 P24072] | * '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P24072 P24072] | ||
Revision as of 13:33, 14 April 2014
- Description: two-component response regulator, modulation of flagellar switch bias
| Gene name | cheY |
| Synonyms | cheB |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component response regulator |
| Function | modulation of flagellar switch bias |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: cheY | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CheY | |
| MW, pI | 13 kDa, 4.746 |
| Gene length, protein length | 360 bp, 120 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | fliY, fliZ |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 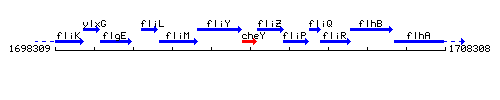
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed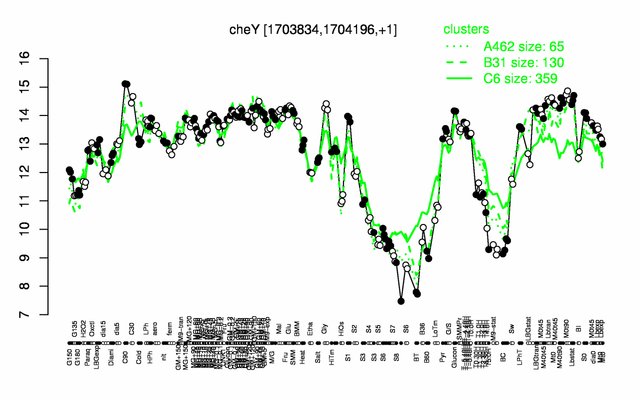
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, motility and chemotaxis, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CodY regulon, SigD regulon, Spo0A regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16330
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16330
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16330
- UniProt: P24072
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- in minimal medium, CheY is present with 7,100 +/- 1,000 molecules per cell PubMed
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Gerald L Hazelbauer, Wing-Cheung Lai
Bacterial chemoreceptors: providing enhanced features to two-component signaling.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2010, 13(2);124-32
[PubMed:20122866]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christopher V Rao, George W Ordal
The molecular basis of excitation and adaptation during chemotactic sensory transduction in bacteria.
Contrib Microbiol: 2009, 16;33-64
[PubMed:19494578]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christopher V Rao, John R Kirby, Adam P Arkin
Phosphatase localization in bacterial chemotaxis: divergent mechanisms, convergent principles.
Phys Biol: 2005, 2(3);148-58
[PubMed:16224120]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original Publications