Difference between revisions of "YcnK"
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU03960&redirect=T BSU03960] | ||
* '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/ycnK.html] | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/ycnK.html] | ||
| Line 94: | Line 95: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU03960&redirect=T BSU03960] | ||
* '''Structure:''' | * '''Structure:''' | ||
Revision as of 12:59, 2 April 2014
| Gene name | ycnK |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcription repressor, DeoR family |
| Function | regulation of copper uptake |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ycnK | |
| MW, pI | 21 kDa, 7.371 |
| Gene length, protein length | 570 bp, 190 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ycnJ, ycnL |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 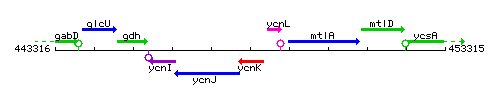
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed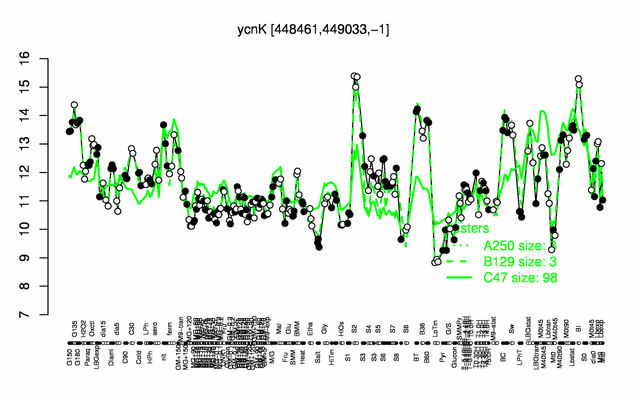
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
trace metal homeostasis (Cu, Zn, Ni, Mn, Mo), transcription factors and their control
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The YcnK regulon:
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU03960
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU03960
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: repression of ycnK-ycnJ-ycnI expression in the presence of excess copper PubMed
- Protein family: DeoR family of transcription factors
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): copper acts as corepressor PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- forms dimers PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU03960
- Structure:
- UniProt: P94433
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Mohamed Marahiel, Marburg University, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Kazutake Hirooka, Takayosh Edahiro, Kosuke Kimura, Yasutaro Fujita
Direct and indirect regulation of the ycnKJI operon involved in copper uptake through two transcriptional repressors, YcnK and CsoR, in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(20);5675-87
[PubMed:22904286]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Pierre Nicolas, Ulrike Mäder, Etienne Dervyn, Tatiana Rochat, Aurélie Leduc, Nathalie Pigeonneau, Elena Bidnenko, Elodie Marchadier, Mark Hoebeke, Stéphane Aymerich, Dörte Becher, Paola Bisicchia, Eric Botella, Olivier Delumeau, Geoff Doherty, Emma L Denham, Mark J Fogg, Vincent Fromion, Anne Goelzer, Annette Hansen, Elisabeth Härtig, Colin R Harwood, Georg Homuth, Hanne Jarmer, Matthieu Jules, Edda Klipp, Ludovic Le Chat, François Lecointe, Peter Lewis, Wolfram Liebermeister, Anika March, Ruben A T Mars, Priyanka Nannapaneni, David Noone, Susanne Pohl, Bernd Rinn, Frank Rügheimer, Praveen K Sappa, Franck Samson, Marc Schaffer, Benno Schwikowski, Leif Steil, Jörg Stülke, Thomas Wiegert, Kevin M Devine, Anthony J Wilkinson, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Michael Hecker, Uwe Völker, Philippe Bessières, Philippe Noirot
Condition-dependent transcriptome reveals high-level regulatory architecture in Bacillus subtilis.
Science: 2012, 335(6072);1103-6
[PubMed:22383849]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shashi Chillappagari, Marcus Miethke, Hein Trip, Oscar P Kuipers, Mohamed A Marahiel
Copper acquisition is mediated by YcnJ and regulated by YcnK and CsoR in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(7);2362-70
[PubMed:19168619]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Mélanie A Hamon, Nicola R Stanley, Robert A Britton, Alan D Grossman, Beth A Lazazzera
Identification of AbrB-regulated genes involved in biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 52(3);847-60
[PubMed:15101989]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)