Difference between revisions of "LeuB"
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| − | + | <br/><br/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
| Line 88: | Line 84: | ||
* '''Kinetic information:''' | * '''Kinetic information:''' | ||
| − | * '''Domains:''' | + | * '''[[Domains]]:''' |
* '''Modification:''' | * '''Modification:''' | ||
** phosphorylated on Arg-4 {{PubMed|22517742}} | ** phosphorylated on Arg-4 {{PubMed|22517742}} | ||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''[[Cofactors]]:''' |
* '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | ||
| Line 119: | Line 115: | ||
* '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=leuB_2891020_2892117_-1 leuB] {{PubMed|22383849}} | * '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=leuB_2891020_2892117_-1 leuB] {{PubMed|22383849}} | ||
| − | * '''Sigma factor:''' [[SigA]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/1577690 PubMed] | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' [[SigA]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/1577690 PubMed] |
| − | * '''Regulation:''' for a complete overview on the regulation of the ilv operon, see [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20935095 Brinsmade ''et al''.] | + | * '''Regulation:''' |
| + | ** for a complete overview on the regulation of the ilv operon, see [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20935095 Brinsmade ''et al''.] | ||
** repressed by casamino acids [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12107147 PubMed] | ** repressed by casamino acids [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12107147 PubMed] | ||
** expression is stimulated in the presence of glucose [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12193635 PubMed] | ** expression is stimulated in the presence of glucose [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12193635 PubMed] | ||
| Line 156: | Line 153: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>15060025,12193635,19258532,8289305,18641142,15547269,12618455,22517742,15547269,12618455,12107147, 20935095</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>15060025,12193635,19258532,8289305,18641142,15547269,12618455,22517742,15547269,12618455,12107147, 20935095 24163341</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 12:25, 22 December 2013
- Description: 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase
| Gene name | leuB |
| Synonyms | leuC |
| Essential | no |
| Product | 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase |
| Function | biosynthesis of leucine |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: leuB | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Ile, Leu, Val, Coenzyme A | |
| MW, pI | 39 kDa, 4.744 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1095 bp, 365 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | leuC, leuA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 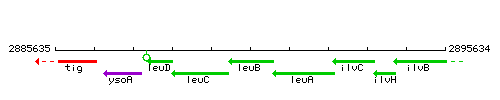
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed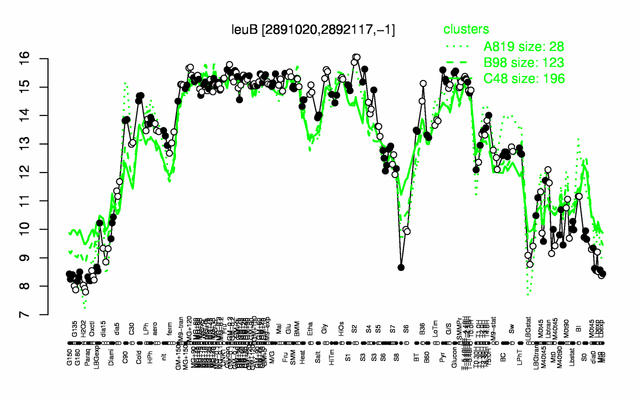
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CcpA regulon, CodY regulon, T-box, TnrA regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28270
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: (2R,3S)-3-isopropylmalate + NAD+ = 4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate + CO2 + NADH (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: LeuB type 1 subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on Arg-4 PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure: 1XAD (Thermus thermophilus)
- UniProt: P05645
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.1.1.85
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- for a complete overview on the regulation of the ilv operon, see Brinsmade et al.
- repressed by casamino acids PubMed
- expression is stimulated in the presence of glucose PubMed
- repressed in the absence of good nitrogen sources (glutamine or ammonium) (TnrA) PubMed
- repressed during growth in the presence of branched chain amino acids (CodY) PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Allison Kriel, Shaun R Brinsmade, Jessica L Tse, Ashley K Tehranchi, Alycia N Bittner, Abraham L Sonenshein, Jue D Wang
GTP dysregulation in Bacillus subtilis cells lacking (p)ppGpp results in phenotypic amino acid auxotrophy and failure to adapt to nutrient downshift and regulate biosynthesis genes.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(1);189-201
[PubMed:24163341]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shaun R Brinsmade, Roelco J Kleijn, Uwe Sauer, Abraham L Sonenshein
Regulation of CodY activity through modulation of intracellular branched-chain amino acid pools.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(24);6357-68
[PubMed:20935095]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ana Gutiérrez-Preciado, Tina M Henkin, Frank J Grundy, Charles Yanofsky, Enrique Merino
Biochemical features and functional implications of the RNA-based T-box regulatory mechanism.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2009, 73(1);36-61
[PubMed:19258532]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shigeo Tojo, Takenori Satomura, Kanako Kumamoto, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Molecular mechanisms underlying the positive stringent response of the Bacillus subtilis ilv-leu operon, involved in the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(18);6134-47
[PubMed:18641142]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shigeo Tojo, Takenori Satomura, Kaori Morisaki, Ken-Ichi Yoshida, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Negative transcriptional regulation of the ilv-leu operon for biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids through the Bacillus subtilis global regulator TnrA.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(23);7971-9
[PubMed:15547269]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulrike Mäder, Susanne Hennig, Michael Hecker, Georg Homuth
Transcriptional organization and posttranscriptional regulation of the Bacillus subtilis branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis genes.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(8);2240-52
[PubMed:15060025]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Yoshiko Nakaura, Robert P Shivers, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Richard Losick, Yasutaro Fujita, Abraham L Sonenshein
Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(6);1911-22
[PubMed:12618455]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Holger Ludwig, Christoph Meinken, Anastasija Matin, Jörg Stülke
Insufficient expression of the ilv-leu operon encoding enzymes of branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis limits growth of a Bacillus subtilis ccpA mutant.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(18);5174-8
[PubMed:12193635]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Knut Büttner, Rüdiger Bode, Michael Hecker
Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(15);4288-95
[PubMed:12107147]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Grundy, T M Henkin
Conservation of a transcription antitermination mechanism in aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and amino acid biosynthesis genes in gram-positive bacteria.
J Mol Biol: 1994, 235(2);798-804
[PubMed:8289305]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)