Difference between revisions of "SepF"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' part of the divisome <br/><br/> | + | * '''Description:''' part of the divisome, recruits [[FtsZ]] to the membrane <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || [[FtsZ]]-interacting protein | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || [[FtsZ]]-interacting protein | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || recruitment of [[FtsZ]] |
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU15390 sepF] | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU15390 sepF] | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| − | + | <br/><br/> | |
= [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
| − | {{SubtiWiki category|[[cell division]]}} | + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[cell division]]}}, |
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[membrane proteins]]}} | ||
= This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| Line 57: | Line 58: | ||
* less efficient cell division results in longer cells. Electron microscopy reveals strongly distorted division septa. | * less efficient cell division results in longer cells. Electron microscopy reveals strongly distorted division septa. | ||
* the ''[[sepF]]'' mutation in combination with a constitutively active form of [[WalR]] ([[WalR]]-R204C) results in the formation of cell wall-less L-forms {{PubMed|22122227}} | * the ''[[sepF]]'' mutation in combination with a constitutively active form of [[WalR]] ([[WalR]]-R204C) results in the formation of cell wall-less L-forms {{PubMed|22122227}} | ||
| + | * the ''sepF'' mutation is synthetically lethal in combination with an ''[[ezrA]]'' mutation or an ''[[ftsA]]'' mutation | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| Line 82: | Line 84: | ||
* '''Domains:''' | * '''Domains:''' | ||
| + | ** N-terminal amphipatic helix for membrane binding {{PubMed|24218584}} | ||
| + | ** C-terminal [[FtsZ]]-binding domain {{PubMed|24218584}} | ||
* '''Modification:''' | * '''Modification:''' | ||
| Line 90: | Line 94: | ||
* '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | * '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | ||
| − | ** [[FtsZ]] (extreme C terminus of [[FtsZ]])-[[SepF]] {{PubMed|22912848,16420366}} | + | ** [[FtsZ]] (extreme C terminus of [[FtsZ]])-[[SepF]] {{PubMed|24218584,22912848,16420366}} |
| − | * '''[[Localization]]:''' septum {{PubMed|16420366}} | + | * '''[[Localization]]:''' |
| + | ** septum {{PubMed|16420366}} | ||
| + | ** membrane {{PubMed|24218584}} | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
* '''Structure:''' | * '''Structure:''' | ||
| + | ** [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3ZIE 3ZIE] (the [[FtsZ]]-binding C-terminal domain of ''Archaeoglobus fulgidus'' [[SepF]]) {{PubMed|24218584}} | ||
* '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O31728 O31728] | * '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O31728 O31728] | ||
| Line 150: | Line 157: | ||
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
| − | + | <pubmed>16420366,16796675,14651647, 24218584 22912848,21224850,22122227</pubmed> | |
| − | <pubmed>16420366,16796675,14651647,</pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 16:53, 13 November 2013
- Description: part of the divisome, recruits FtsZ to the membrane
| Gene name | sepF |
| Synonyms | ylmF |
| Essential | no |
| Product | FtsZ-interacting protein |
| Function | recruitment of FtsZ |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: sepF | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SepF | |
| MW, pI | 17 kDa, 4.863 |
| Gene length, protein length | 447 bp, 149 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ylmE, ylmG |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 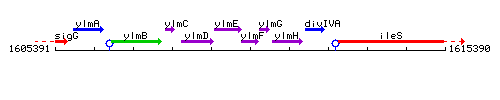
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15390
Phenotypes of a mutant
- perturbation of the formation of properly formed division septa
- less efficient cell division results in longer cells. Electron microscopy reveals strongly distorted division septa.
- the sepF mutation in combination with a constitutively active form of WalR (WalR-R204C) results in the formation of cell wall-less L-forms PubMed
- the sepF mutation is synthetically lethal in combination with an ezrA mutation or an ftsA mutation
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: sepF family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: O31728
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Leendert Hamoen, CBCB, Newcastle University, UK
Shu Ishikawa, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, Nara, Japan
Your additional remarks
SepF mutation is synthetic lethal in combination with an ezrA mutation or an ftsA mutation.
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Ramona Duman, Shu Ishikawa, Ilkay Celik, Henrik Strahl, Naotake Ogasawara, Paulina Troc, Jan Löwe, Leendert W Hamoen
Structural and genetic analyses reveal the protein SepF as a new membrane anchor for the Z ring.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2013, 110(48);E4601-10
[PubMed:24218584]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ewa Cendrowicz, Sebastiaan P van Kessel, Laura S van Bezouwen, Neeraj Kumar, Egbert J Boekema, Dirk-Jan Scheffers
Bacillus subtilis SepF binds to the C-terminus of FtsZ.
PLoS One: 2012, 7(8);e43293
[PubMed:22912848]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Patricia Domínguez-Cuevas, Romain Mercier, Mark Leaver, Yoshikazu Kawai, Jeff Errington
The rod to L-form transition of Bacillus subtilis is limited by a requirement for the protoplast to escape from the cell wall sacculus.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 83(1);52-66
[PubMed:22122227]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Muhammet E Gündoğdu, Yoshikazu Kawai, Nada Pavlendova, Naotake Ogasawara, Jeff Errington, Dirk-Jan Scheffers, Leendert W Hamoen
Large ring polymers align FtsZ polymers for normal septum formation.
EMBO J: 2011, 30(3);617-26
[PubMed:21224850]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shu Ishikawa, Yoshikazu Kawai, Konosuke Hiramatsu, Masayoshi Kuwano, Naotake Ogasawara
A new FtsZ-interacting protein, YlmF, complements the activity of FtsA during progression of cell division in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 60(6);1364-80
[PubMed:16796675]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Leendert W Hamoen, Jean-Christophe Meile, Wouter de Jong, Philippe Noirot, Jeff Errington
SepF, a novel FtsZ-interacting protein required for a late step in cell division.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 59(3);989-99
[PubMed:16420366]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Masaya Fujita, Shane T Jensen, Patrick Eichenberger, José E González-Pastor, Jun S Liu, Richard Losick
The Spo0A regulon of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 50(5);1683-701
[PubMed:14651647]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)