Difference between revisions of "SspA"
(→Biological materials) |
|||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
| + | ** BP137 (cat)available in [[Fabian Commichau]]'s lab | ||
** 1S109 (no resistance), available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1S109&Search=1S109 BGSC] | ** 1S109 (no resistance), available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1S109&Search=1S109 BGSC] | ||
** 1S111 (no resistance), {{PubMed|3087950}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1S111&Search=1S111 BGSC] | ** 1S111 (no resistance), {{PubMed|3087950}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1S111&Search=1S111 BGSC] | ||
Revision as of 13:47, 11 July 2013
- Description: small acid-soluble spore protein (major alpha-type SASP)
| Gene name | sspA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | small acid-soluble spore protein (major alpha-type SASP) |
| Function | protection of spore DNA |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: sspA | |
| MW, pI | 6 kDa, 4.731 |
| Gene length, protein length | 207 bp, 69 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ytcI, thiI |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 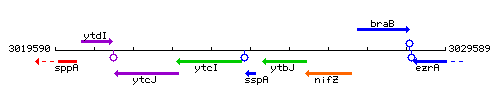
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed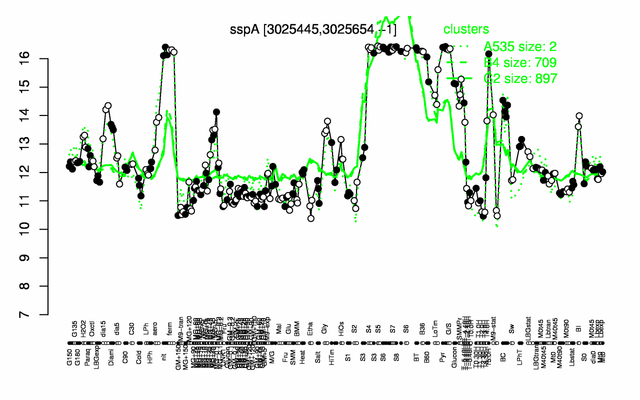
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29570
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: alpha/beta-type SASP family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure: 2BZ0 (82% identity, 89% similarity)
- UniProt: P04831
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information: the mRNA is very stable (half-life > 15 min) PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Ralf Moeller, Andrew C Schuerger, Günther Reitz, Wayne L Nicholson
Protective role of spore structural components in determining Bacillus subtilis spore resistance to simulated mars surface conditions.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2012, 78(24);8849-53
[PubMed:23064347]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ralf Moeller, Peter Setlow, Günther Reitz, Wayne L Nicholson
Roles of small, acid-soluble spore proteins and core water content in survival of Bacillus subtilis spores exposed to environmental solar UV radiation.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2009, 75(16);5202-8
[PubMed:19542328]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Barbara Setlow, Swaroopa Atluri, Ryan Kitchel, Kasia Koziol-Dube, Peter Setlow
Role of dipicolinic acid in resistance and stability of spores of Bacillus subtilis with or without DNA-protective alpha/beta-type small acid-soluble proteins.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(11);3740-7
[PubMed:16707666]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Leif Steil, Mónica Serrano, Adriano O Henriques, Uwe Völker
Genome-wide analysis of temporally regulated and compartment-specific gene expression in sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2005, 151(Pt 2);399-420
[PubMed:15699190]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Thierry Douki, Barbara Setlow, Peter Setlow
Effects of the binding of alpha/beta-type small, acid-soluble spore proteins on the photochemistry of DNA in spores of Bacillus subtilis and in vitro.
Photochem Photobiol: 2005, 81(1);163-9
[PubMed:15458366]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Hambraeus, C von Wachenfeldt, L Hederstedt
Genome-wide survey of mRNA half-lives in Bacillus subtilis identifies extremely stable mRNAs.
Mol Genet Genomics: 2003, 269(5);706-14
[PubMed:12884008]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B Setlow, K A McGinnis, K Ragkousi, P Setlow
Effects of major spore-specific DNA binding proteins on Bacillus subtilis sporulation and spore properties.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(24);6906-12
[PubMed:11092849]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
I Bagyan, J Hobot, S Cutting
A compartmentalized regulator of developmental gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(15);4500-7
[PubMed:8755877]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B Setlow, P Setlow
Binding to DNA protects alpha/beta-type, small, acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus and Clostridium species against digestion by their specific protease as well as by other proteases.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(14);4149-51
[PubMed:7608092]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J M Mason, P Fajardo-Cavazos, P Setlow
Levels of mRNAs which code for small, acid-soluble spore proteins and their LacZ gene fusions in sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 1988, 16(14A);6567-83
[PubMed:2456528]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R H Hackett, P Setlow
Properties of spores of Bacillus subtilis strains which lack the major small, acid-soluble protein.
J Bacteriol: 1988, 170(3);1403-4
[PubMed:3125155]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J M Mason, P Setlow
Essential role of small, acid-soluble spore proteins in resistance of Bacillus subtilis spores to UV light.
J Bacteriol: 1986, 167(1);174-8
[PubMed:3087950]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M J Connors, J M Mason, P Setlow
Cloning and nucleotide sequencing of genes for three small, acid-soluble proteins from Bacillus subtilis spores.
J Bacteriol: 1986, 166(2);417-25
[PubMed:3009398]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)