Difference between revisions of "FloT"
(→References) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 151: | Line 151: | ||
'''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|22178969}} | '''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|22178969}} | ||
<pubmed>9987136,22753055, 12107147, 18763711, 19383680 </pubmed> | <pubmed>9987136,22753055, 12107147, 18763711, 19383680 </pubmed> | ||
| − | <pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 22882210 ,23249255 </pubmed> |
| + | <pubmed> 20713508 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 14:31, 3 January 2013
- Description: similar to flotillin 1, orchestration of physiological processes in lipid microdomains, involved in the control of membrane fluidity, confers (together with YuaF) resistance to cefuroxime
| Gene name | floT |
| Synonyms | yuaG, yuaH |
| Essential | no |
| Product | bacterial flotillin-like protein |
| Function | involved in the control of membrane fluidity |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: floT | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: FloT | |
| MW, pI | 55 kDa, 5.135 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1527 bp, 509 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yuaI, yuaF |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 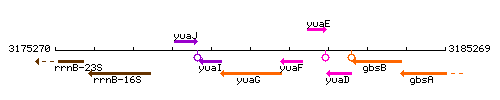
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed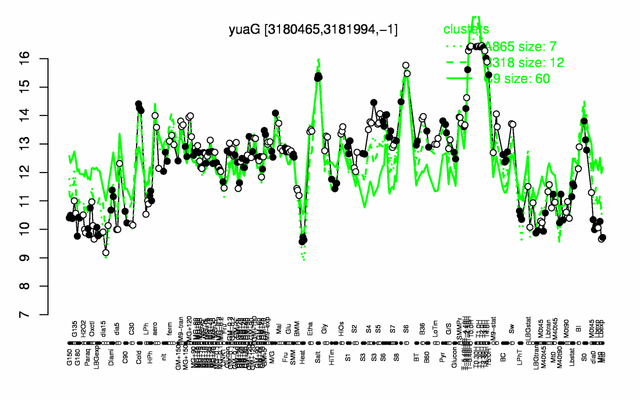
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biofilm formation, membrane dynamics, membrane proteins sporulation/ other, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y)
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU31010
Phenotypes of a mutant
- delayed onset of sporulation, reduced sporulation frequency
- defect in motility PubMed
- a floT floA double mutant does not induce KinC-dependent biofilm formation upon addition of surfactin PubMed
- a floT floA double mutant has a strong synthetic defect in motility, cell morphology, and transformation efficiency PubMed
- a floT floA double mutant has a sporulation defect, due to the lack of FtsH PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O32076
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Felix Dempwolff, Heiko M Möller, Peter L Graumann
Synthetic motility and cell shape defects associated with deletions of flotillin/reggie paralogs in Bacillus subtilis and interplay of these proteins with NfeD proteins.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(17);4652-61
[PubMed:22753055]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Catriona Donovan, Marc Bramkamp
Characterization and subcellular localization of a bacterial flotillin homologue.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 6);1786-1799
[PubMed:19383680]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Knut Büttner, Rüdiger Bode, Michael Hecker
Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(15);4288-95
[PubMed:12107147]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
X Huang, A Gaballa, M Cao, J D Helmann
Identification of target promoters for the Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic function sigma factor, sigma W.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 31(1);361-71
[PubMed:9987136]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Felix Dempwolff, Hanna M Wischhusen, Mara Specht, Peter L Graumann
The deletion of bacterial dynamin and flotillin genes results in pleiotrophic effects on cell division, cell growth and in cell shape maintenance.
BMC Microbiol: 2012, 12;298
[PubMed:23249255]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Ana Yepes, Johannes Schneider, Benjamin Mielich, Gudrun Koch, Juan-Carlos García-Betancur, Kumaran S Ramamurthi, Hera Vlamakis, Daniel López
The biofilm formation defect of a Bacillus subtilis flotillin-defective mutant involves the protease FtsH.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 86(2);457-71
[PubMed:22882210]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)