Difference between revisions of "WalK"
(→Original Publications) |
(→Original Publications) |
||
| Line 148: | Line 148: | ||
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>18573169,17350627,17827301,9829949,17581128,10878122,16030236,12950927,18408157, 19342776 20057515 20059685 20167622 21219466 | + | '''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|22526318}} |
| + | <pubmed>18573169,17350627,17827301,9829949,17581128,10878122,16030236,12950927,18408157, 19342776 20057515 20059685 20167622 21219466 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 10:10, 27 April 2012
- Description: two-component sensor kinase, controls cell wall metabolism, co-ordinates cell wall remodelling with cell division by controlling the transcription of genes for autolysins and their inhibitors
| Gene name | walK |
| Synonyms | yycG |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase (OmpR family) |
| Function | control of cell wall metabolism |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: WalK | |
| MW, pI | 69 kDa, 4.775 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1833 bp, 611 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yycH, walR |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 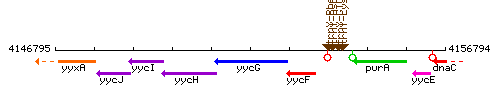
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed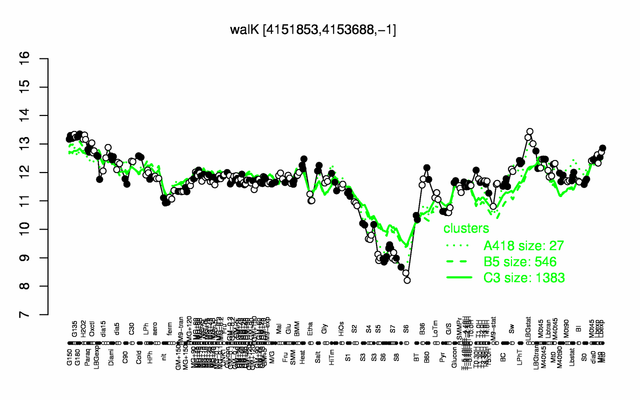
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall/ other, protein modification, transcription factors and their control, essential genes, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU40400
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: autophosphorylation, phosphorylation of WalR
- Protein family: two-component sensor kinase of the OmpR family
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: two transmembrane segments, C-terminal histidine phosphotransferase domain
- Modification: autophosphorylation on a His residue
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: Q45614
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation: expressed during vegetative growth, repressed during stationary phase PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Sarah Dubrac, Paola Bisicchia, Kevin M Devine, Tarek Msadek
A matter of life and death: cell wall homeostasis and the WalKR (YycGF) essential signal transduction pathway.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 70(6);1307-22
[PubMed:19019149]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sarah Dubrac, Tarek Msadek
Tearing down the wall: peptidoglycan metabolism and the WalK/WalR (YycG/YycF) essential two-component system.
Adv Exp Med Biol: 2008, 631;214-28
[PubMed:18792692]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Malcolm E Winkler, James A Hoch
Essentiality, bypass, and targeting of the YycFG (VicRK) two-component regulatory system in gram-positive bacteria.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(8);2645-8
[PubMed:18245295]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original Publications
Additional publications: PubMed