Difference between revisions of "CcpA"
(→General and physiological studies) |
(→Extended information on the protein) |
||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
* '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | * '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | ||
| − | ** CcpA-[[PtsH |HPr]] {{PubMed|15369672}} | + | ** [[CcpA]]-[[PtsH |HPr]] {{PubMed|15369672}} |
| − | ** CcpA-[[Crh]] {{PubMed|16316990}} | + | ** [[CcpA]]-[[Crh]] {{PubMed|16316990}} |
| − | ** CcpA-[[RpoA]] {{PubMed|22512862}} | + | ** [[CcpA]]-[[RpoA]] {{PubMed|22512862}} |
| − | ** CcpA-[[CodY]] {{PubMed|22512862}} | + | ** [[CcpA]]-[[CodY]] {{PubMed|22512862}} |
* '''[[Localization]]:''' | * '''[[Localization]]:''' | ||
Revision as of 08:49, 20 April 2012
- Description: Carbon catabolite control protein A, involved in glucose regulation of many genes; represses catabolic genes and activates genes involved in excretion of excess carbon
| Gene name | ccpA |
| Synonyms | graR, alsA, amyR |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator (LacI family) |
| Function | mediates carbon catabolite repression (CCR) |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CcpA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Nucleoside catabolism, Nucleotides (regulation), Ile, Leu, Val, His, Coenzyme A, Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 36,8 kDa, 5.06 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1002 bp, 334 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | motP, aroA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 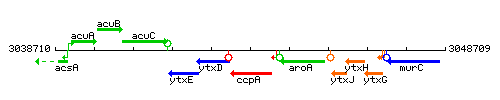
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
- 1 Categories containing this gene/protein
- 2 This gene is a member of the following regulons
- 3 The CcpA regulon
- 4 The gene
- 5 The protein
- 6 Expression and regulation
- 7 Biological materials
- 8 Labs working on this gene/protein
- 9 Your additional remarks
- 10 References
- 10.1 Reviews
- 10.2 General and physiological studies
- 10.3 Global analyses (proteome, transcriptome, ChIP-chip)
- 10.4 Repression of target genes by CcpA
- 10.5 Positive regulation of gene expression by CcpA
- 10.6 Control of CcpA activity
- 10.7 CcpA-DNA interaction
- 10.8 Functional analysis of CcpA
- 10.9 Structural analyses
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, regulators of core metabolism
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The CcpA regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29740
Phenotypes of a mutant
Loss of carbon catabolite repression. Loss of PTS-dependent sugar transport due to excessive phosphorylation of HPr by HprK. The mutant is unable to grow on a minimal medium with glucose and ammonium as the only sources of carbon and nitrogen, respectively.
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: transcriptional regulator of carbon catabolite repression (CCR)
- Protein family: LacI family
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- HTH LacI-type Domain (1 – 58)
- DNA binding Domain (6 – 25)
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate Pubmed
Database entries
- Structure:
- 2JCG (Apoprotein from Bacillus megaterium)
- CcpA-Crh-DNA-complex NCBI
- complex with P-Ser-HPr and sulphate ions NCBI
- 3OQM (complex of B. subtilis CcpA with P-Ser-HPr and the ackA operator site)
- 3OQN (complex of B. subtilis CcpA with P-Ser-HPr and the gntR operator site)
- 3OQO (complex of B. subtilis CcpA with P-Ser-HPr and a optimal synthetic operator site)
- UniProt: P25144
- KEGG entry: [3]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation: constitutively expressed PubMed
- Additional information: there are about 3.000 molecules of CcpA per cell PubMed, this corresponds to a concentration of 3 myM (according to PubMed)
Biological materials
- Mutant: QB5407 (spc), GP302 (erm), GP300 (an in frame deletion of ccpA), available in Stülke lab; WH649 (aphA3), available in Gerald Seidel's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Gerald Seidel, Erlangen University, Germany Homepage
- Richard Brennan, Houston, Texas, USA Homepage
- Milton H. Saier, University of California at San Diego, USA Homepage
- Yasutaro Fujita, University of Fukuyama, Japan
- Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
- Oscar Kuipers, University of Groningen, The Netherlands Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
General and physiological studies
Additional publications: PubMed
Global analyses (proteome, transcriptome, ChIP-chip)
Repression of target genes by CcpA
Additional publications: PubMed
Positive regulation of gene expression by CcpA
Control of CcpA activity
CcpA-DNA interaction
Functional analysis of CcpA
Structural analyses