Difference between revisions of "PyrC"
m (Reverted edits by 134.76.70.252 (talk) to last revision by Jstuelk) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
* '''Locus tag:''' BSU15500 | * '''Locus tag:''' BSU15500 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
Revision as of 09:02, 28 January 2012
- Description: dihydroorotase
| Gene name | pyrC |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | dihydroorotase |
| Function | pyrimidine biosynthesis |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Pyrimidines, Nucleotides (regulation) | |
| MW, pI | 46 kDa, 5.427 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1284 bp, 428 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | pyrB, pyrAA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 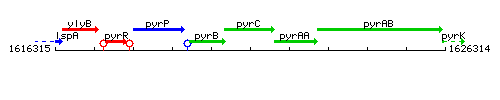
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of nucleotides
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15500
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: (S)-dihydroorotate + H2O = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: Type 2 subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): PucH
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure: 3GRI (from Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus mw2, 60% identity, 72% similarity)
- UniProt: P25995
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 3.5.2.3
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- PyrR: RNA switch, transcription termination/ antitermination (in the presence of uridine nucleotides: termination, in their absence: antitermination) PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
R J Turner, Y Lu, R L Switzer
Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis pyrimidine biosynthetic (pyr) gene cluster by an autogenous transcriptional attenuation mechanism.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(12);3708-22
[PubMed:8206849]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C L Quinn, B T Stephenson, R L Switzer
Functional organization and nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis pyrimidine biosynthetic operon.
J Biol Chem: 1991, 266(14);9113-27
[PubMed:1709162]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)