Difference between revisions of "ProB"
m (Reverted edits by 134.76.70.252 (talk) to last revision by Jstuelk) |
|||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
* '''Locus tag:''' BSU13120 | * '''Locus tag:''' BSU13120 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
Revision as of 08:44, 28 January 2012
- Description: glutamate 5-kinase
| Gene name | proB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | glutamate 5-kinase |
| Function | biosynthesis of proline |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Pro, Stress | |
| MW, pI | 39 kDa, 6.01 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1095 bp, 365 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ykkE, proA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 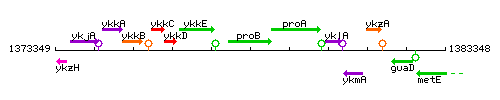
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13120
Phenotypes of a mutant
- auxotrophic for proline PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + L-glutamate = ADP + L-glutamate 5-phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: PUA domain (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): ProJ
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: the enzymatic activity is feedback-inhibited by proline {PubMed|16958849}}
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39820
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 2.7.2.11
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- T-box: RNA switch, transcriptional antitermination PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Jeanette Brill, Tamara Hoffmann, Harald Putzer, Erhard Bremer
T-box-mediated control of the anabolic proline biosynthetic genes of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2011, 157(Pt 4);977-987
[PubMed:21233158]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ana Gutiérrez-Preciado, Tina M Henkin, Frank J Grundy, Charles Yanofsky, Enrique Merino
Biochemical features and functional implications of the RNA-based T-box regulatory mechanism.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2009, 73(1);36-61
[PubMed:19258532]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Mingqing Chen, Hongbo Wei, JunWei Cao, Ruijie Liu, Youliang Wang, Congyi Zheng
Expression of Bacillus subtilis proBA genes and reduction of feedback inhibition of proline synthesis increases proline production and confers osmotolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis.
J Biochem Mol Biol: 2007, 40(3);396-403
[PubMed:17562291]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Mingqing Chen, Junwei Cao, Congyi Zheng, Qing Liu
Directed evolution of an artificial bifunctional enzyme, gamma-glutamyl kinase/gamma-glutamyl phosphate reductase, for improved osmotic tolerance of Escherichia coli transformants.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2006, 263(1);41-7
[PubMed:16958849]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)