Difference between revisions of "PonA"
(→Categories containing this gene/protein) |
|||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
= [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
{{SubtiWiki category|[[cell wall synthesis]]}}, | {{SubtiWiki category|[[cell wall synthesis]]}}, | ||
| − | {{SubtiWiki category|[[cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, W, X, Y)]]}}, | + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y)]]}}, |
{{SubtiWiki category|[[membrane proteins]]}} | {{SubtiWiki category|[[membrane proteins]]}} | ||
Revision as of 22:10, 24 August 2011
- Description: penicillin-binding protein 1A/1B
| Gene name | ponA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | penicillin-binding protein 1A/1B |
| Function | bifunctional glucosyltransferase/ transpeptidase |
| MW, pI | 99 kDa, 4.752 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2742 bp, 914 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | recU, ypoC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 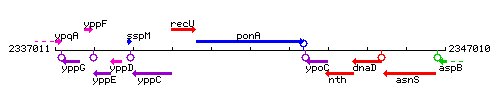
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU22320
Phenotypes of a mutant
- prevents bulging of the cells when grown at low Mg(2+) concentrations, suppresses the lethal effect of a mreB mutation PubMed
- deletion of ponA restores growth and normal shape of a yvcK mutant on gluconeogenic carbon sources PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39793
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: constitutive during vegetative growth PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jeff Errington lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jeff Errington, Newcastle University, UK homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications