Difference between revisions of "SacT"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' [[PRD-containing transcription factors|transcriptional antiterminator]] for the ''[[sacP]]-[[sacA]]'' operon <br/><br/> | + | * '''Description:''' [[PRD-containing transcription factors|transcriptional antiterminator]] for the ''[[sacP]]-[[sacA]]-[[ywdA]]'' operon <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
= This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| − | + | =The [[SacT regulon]]: ''[[sacP]]-[[sacA]]-[[ywdA]]''= | |
=The gene= | =The gene= | ||
Revision as of 12:07, 5 February 2011
- Description: transcriptional antiterminator for the sacP-sacA-ywdA operon
| Gene name | sacT |
| Synonyms | ipa-47d |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional antiterminator |
| Function | regulation of sucrose utilization |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Sugar catabolism, Stress | |
| MW, pI | 31 kDa, 5.587 |
| Gene length, protein length | 828 bp, 276 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ywcJ, ywcI |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 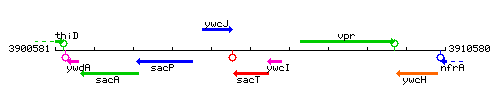
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of specific carbon sources, transcription factors and their control, RNA binding regulators, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The SacT regulon: sacP-sacA-ywdA
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU38070
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: binding to the mRNA of the sacP-sacA operon, causes transcription antitermination (in presence of sucrose and absence of glucose)
- Protein family: transcriptional antiterminator bglG family (according to Swiss-Prot) BglG family of antiterminators
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P26212
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- repressed by casamino acids PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP429 (spc), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- for expression, purification of both PRDs in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP166, available in Stülke lab
- for expression, purification of PRD-1 in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP426, available in Stülke lab
- for expression, purification of PRD-2 in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP427, available in Stülke lab
- for expression, purification of PRD-1 in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag and thrombin cleavage site, in pGP570: pGP439, available in Stülke lab
- for expression, purification of PRD-2 in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag and thrombin cleavage site, in pGP570: pGP440, available in Stülke lab
- for expression, purification of the RNA-binding domain in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag and thrombin cleavage site, in pGP570: pGP571, available in Stülke lab
- for expression of the RNA-binding domain in B. subtilis, in pBQ200: pGP446, available in Stülke lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References