Difference between revisions of "McpB"
(→Extended information on the protein) |
|||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
* '''Domains:''' | * '''Domains:''' | ||
| − | * '''Modification:''' | + | * '''Modification:''' methylated at residues Gln371, Glu630, and Glu637 {{PubMed|20864474}} |
* '''Cofactor(s):''' | * '''Cofactor(s):''' | ||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>11722727,10825179,8251536,12909020,10196193,15544802,6137212,9194713,2505839,8188684,2105313,12123464,14731274,,18763711, 19864420 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>11722727,10825179,8251536,12909020,10196193,15544802,6137212,9194713,2505839,8188684,2105313,12123464,14731274,20864474 ,18763711, 19864420 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 17:22, 25 September 2010
- Description: methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein
| Gene name | mcpB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein |
| Function | control of chemotaxis |
| MW, pI | 71 kDa, 5.13 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1986 bp, 662 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | tlpA, tgl |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 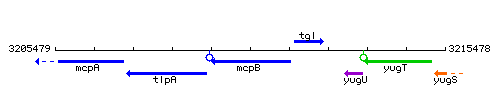
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU31260
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: K(D) for asparagine: 14 myM PubMed
- Domains:
- Modification: methylated at residues Gln371, Glu630, and Glu637 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: asparagine (binds to the part of McpB that is exposed to the exterior) PubMed
- Localization: cell membrane PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39215
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References