Difference between revisions of "Rny"
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
* '''Interactions:''' [[Rny]]-[[PfkA]], [[Rny]]-[[Eno]], [[Rny]]-[[PnpA]], [[Rny]]-[[RnjA]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/19193632 PubMed] | * '''Interactions:''' [[Rny]]-[[PfkA]], [[Rny]]-[[Eno]], [[Rny]]-[[PnpA]], [[Rny]]-[[RnjA]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/19193632 PubMed] | ||
| − | * '''Localization:''' cell membrane, single-pass membrane protein | + | * '''Localization:''' cell membrane, single-pass membrane protein {{PubMed|18763711,17005971,19820159}} |
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| Line 137: | Line 137: | ||
| − | <pubmed>18763711,19193632,17005971 19779461 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>18763711,19193632,17005971 19779461 19820159 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 08:51, 13 October 2009
- Description: RNase Y, 5' end sensitive endoribonuclease, involved in the degradation/processing of mRNA
| Gene name | rny |
| Synonyms | ymdA |
| Essential | yes |
| Product | RNase Y |
| Function | Initiates S-box riboswitch RNA turnover, required for the processing of the gapA operon mRNA, depletion of RNase Y increases bulk mRNA stability. |
| Regulatory function of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 58,7 kDa, 5.39 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1560 bp, 520 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | pbpX, ymdB |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 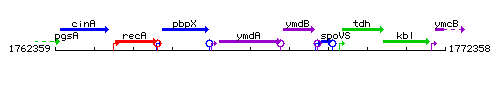
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16960
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: RNase Y cleaves S-box riboswitch RNAs in vivo and in vitro; preference for 5' monophosphorylated substrate in vitro, endonucleolytic cleavage; required for the processing of the gapA operon mRNA PubMed, cleavage activity appears sensitive to downstream secondary structure.
- Protein family: Member of the HD superfamily of metal-dependent phosphohydrolases; 2',3' cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- transmembrane domain (4–24)
- KH domain (210–273)
- HD domain (336–429)
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): requires Mg+2, which can be replaced by Zn+2 or Mn+2 ions
- Effectors of protein activity: appears sensitive to downstream secondary structure
- Localization: cell membrane, single-pass membrane protein PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O31774
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 3.1.4.16
Additional information
required for the processing of the gapA operon mRNA
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation: constitutive
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information: there is a terminator between rny and ymdB, most transcripts terminate there
Biological materials
- Mutant: essential!!!!, 4043 (rny under p-spac control, cat), GP193 (rny under p-xyl control, cat), both available in Stülke lab; SSB447 (rny under P-spac control, "erm") available in Putzer lab.
- Expression vector:
- N-terminal Strep-tag, expression in E. coli, in pGP172: pGP441, available in Stülke lab
- N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, expression in B. subtilis, in pGP380: pGP775 , available in Stülke lab
- Expression of RNase Y missing the N-terminal transmembrane domain (25aa) as an intein fusion in E. coli (no tag left in the purified protein) available in the Putzer lab
- wild type rny, expression in B. subtilis, in pBQ200: pGP1201, available in Stülke lab
- there is also a series of domain constructs present in pBQ200, all available in Stülke lab
- GFP fusion: B. subtilis 3569 (amyE:: (p-xyl rny-gfpmut1-spc)), available in Errington lab
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Harald Putzer, IBPC Paris, France Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Jessica C Zweers, Thomas Wiegert, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Stress-responsive systems set specific limits to the overproduction of membrane proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2009, 75(23);7356-64
[PubMed:19820159]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Karen Shahbabian, Ailar Jamalli, Léna Zig, Harald Putzer
RNase Y, a novel endoribonuclease, initiates riboswitch turnover in Bacillus subtilis.
EMBO J: 2009, 28(22);3523-33
[PubMed:19779461]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Fabian M Rothe, Christina Herzberg, Eva Wagner, Daniel Hellwig, Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Elke Hammer, Uwe Völker, Jörg Stülke
Novel activities of glycolytic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: interactions with essential proteins involved in mRNA processing.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2009, 8(6);1350-60
[PubMed:19193632]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alison Hunt, Joy P Rawlins, Helena B Thomaides, Jeff Errington
Functional analysis of 11 putative essential genes in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2006, 152(Pt 10);2895-2907
[PubMed:17005971]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)