Difference between revisions of "Sda"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' developmental checkpoint protein, inhibits the autokinase activity of [[KinA]] | + | * '''Description:''' developmental checkpoint protein, inhibits the autokinase activity of [[KinA]] |
| + | |||
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
| Line 56: | Line 57: | ||
=== Basic information/ Evolution === | === Basic information/ Evolution === | ||
| − | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' Sda is a checkpoint protein that is upregulated in response to replication stress {{PubMed|11207367}}. Sda inhibits the autokinase activity of [[KinA]] (and likely [[KinB]] as well). This in its turn results in reduced levels of [[Spo0A|Spo0A~P]]. Thus, replication stressed cells will not initiate sporulation | + | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' Sda is a checkpoint protein that is upregulated in response to replication stress {{PubMed|11207367}}. Sda inhibits the autokinase activity of [[KinA]] (and likely [[KinB]] as well). This in its turn results in reduced levels of [[Spo0A|Spo0A~P]]. Thus, replication stressed cells will not initiate sporulation. |
| − | |||
* '''Protein family:''' | * '''Protein family:''' | ||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sda is rapidly turned over by the [[ClpP|ClpP/X]] system because of some uncharged residues at its C-terminus {{PubMed|16796683}}. | ||
=Expression and regulation= | =Expression and regulation= | ||
| Line 103: | Line 105: | ||
** [[LexA]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16267290 PubMed] | ** [[LexA]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16267290 PubMed] | ||
| − | * '''Additional information:''' | + | * '''Additional information:''' Sda is rapidly turned over by the [[ClpP|ClpP/X]] system because of some uncharged residues at its C-terminus {{PubMed|16796683}}. |
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
Revision as of 22:17, 29 July 2009
- Description: developmental checkpoint protein, inhibits the autokinase activity of KinA
| Gene name | sda |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | developmental checkpoint protein |
| Function | mediates a developmental checkpoint coupling initiation of sporulation (phosphorylation of Spo0A) to the function of replication initiation proteins |
| MW, pI | 6 kDa, 5.605 |
| Gene length, protein length | 156 bp, 52 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yloV, sdaAA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 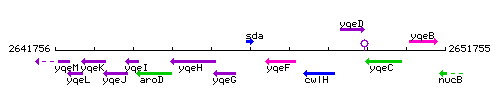
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU25690
Phenotypes of a mutant
- sporulates at a higher frequency
- will sporulate in the presence of replication stress
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Sda is a checkpoint protein that is upregulated in response to replication stress PubMed. Sda inhibits the autokinase activity of KinA (and likely KinB as well). This in its turn results in reduced levels of Spo0A~P. Thus, replication stressed cells will not initiate sporulation.
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- UniProt: Q7WY62
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Sda is rapidly turned over by the ClpP/X system because of some uncharged residues at its C-terminus PubMed.
Expression and regulation
- Operon: sda
- Sigma factor: SigA
- Regulatory mechanism: Probably activated by DnaA under replication stress
- Additional information: Sda is rapidly turned over by the ClpP/X system because of some uncharged residues at its C-terminus PubMed.
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Bill Burkholder Homepage
Your additional remarks
References