Difference between revisions of "LytF"
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
* '''Kinetic information:''' | * '''Kinetic information:''' | ||
| − | * '''Domains:''' | + | * '''[[Domains]]:''' |
| + | ** contains four N-acetylglucosamine-polymer-binding [[LysM domain]]s {{PubMed|18430080}} | ||
** C-terminal D,L-endopeptidase domain {{PubMed|22139507}} | ** C-terminal D,L-endopeptidase domain {{PubMed|22139507}} | ||
* '''Modification:''' | * '''Modification:''' | ||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''[[Cofactors]]:''' |
* '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | ||
| Line 143: | Line 144: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| + | == Reviews== | ||
| + | <pubmed>18430080</pubmed> | ||
| + | == Original publications == | ||
<pubmed> 20351052,10322020,10206711,14594841,18761696, 19542270 22139507 23855774 23091053</pubmed> | <pubmed> 20351052,10322020,10206711,14594841,18761696, 19542270 22139507 23855774 23091053</pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 14:46, 27 December 2013
- Description: gamma-D-glutamate-meso-diaminopimelate muropeptidase (major autolysin)
| Gene name | lytF |
| Synonyms | cwlE, yhdD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | gamma-D-glutamate-meso-diaminopimelate muropeptidase (major autolysin) |
| Function | cell separation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: lytF | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: LytF | |
| MW, pI | 51 kDa, 10.41 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1464 bp, 488 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yhdC, nsrR |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 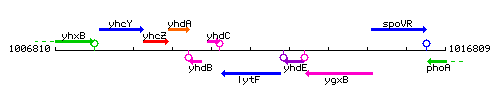
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed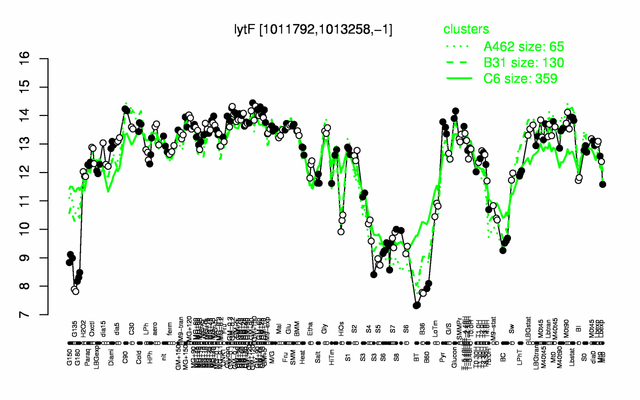
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall degradation/ turnover
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU09370
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: nlpC/p60 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): the C-terminal D,L-endopeptidase domains of LytE, LytF, CwlS, and CwlO exhibit strong sequence similarity
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- contains four N-acetylglucosamine-polymer-binding LysM domains PubMed
- C-terminal D,L-endopeptidase domain PubMed
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- secreted (according to Swiss-Prot)
- localizes to cell septa and poles PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O07532
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Girbe Buist, Anton Steen, Jan Kok, Oscar P Kuipers
LysM, a widely distributed protein motif for binding to (peptido)glycans.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 68(4);838-47
[PubMed:18430080]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
Jeffrey Meisner, Paula Montero Llopis, Lok-To Sham, Ethan Garner, Thomas G Bernhardt, David Z Rudner
FtsEX is required for CwlO peptidoglycan hydrolase activity during cell wall elongation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 89(6);1069-83
[PubMed:23855774]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ryoichi Arai, Sadaharu Fukui, Naoya Kobayashi, Junichi Sekiguchi
Solution structure of IseA, an inhibitor protein of DL-endopeptidases from Bacillus subtilis, reveals a novel fold with a characteristic inhibitory loop.
J Biol Chem: 2012, 287(53);44736-48
[PubMed:23091053]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Masayuki Hashimoto, Seika Ooiwa, Junichi Sekiguchi
Synthetic lethality of the lytE cwlO genotype in Bacillus subtilis is caused by lack of D,L-endopeptidase activity at the lateral cell wall.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(4);796-803
[PubMed:22139507]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yunrong Chai, Thomas Norman, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
An epigenetic switch governing daughter cell separation in Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 2010, 24(8);754-65
[PubMed:20351052]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Rui Chen, Sarah B Guttenplan, Kris M Blair, Daniel B Kearns
Role of the sigmaD-dependent autolysins in Bacillus subtilis population heterogeneity.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(18);5775-84
[PubMed:19542270]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hiroki Yamamoto, Yukiko Miyake, Miharu Hisaoka, Shin-Ichirou Kurosawa, Junichi Sekiguchi
The major and minor wall teichoic acids prevent the sidewall localization of vegetative DL-endopeptidase LytF in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 70(2);297-310
[PubMed:18761696]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hiroki Yamamoto, Shin-ichirou Kurosawa, Junichi Sekiguchi
Localization of the vegetative cell wall hydrolases LytC, LytE, and LytF on the Bacillus subtilis cell surface and stability of these enzymes to cell wall-bound or extracellular proteases.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(22);6666-77
[PubMed:14594841]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R Ohnishi, S Ishikawa, J Sekiguchi
Peptidoglycan hydrolase LytF plays a role in cell separation with CwlF during vegetative growth of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(10);3178-84
[PubMed:10322020]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Philippe Margot, Marco Pagni, Dimitri Karamata
Bacillus subtilis 168 gene lytF encodes a gamma-D-glutamate-meso-diaminopimelate muropeptidase expressed by the alternative vegetative sigma factor, sigmaD.
Microbiology (Reading): 1999, 145 ( Pt 1);57-65
[PubMed:10206711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)