Difference between revisions of "YycI"
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
<div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | <div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" |'''[http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=yycI_4149667_4150509_-1 Expression at a glance]'''   {{PubMed|22383849}}<br/>[[Image:yycI_expression.png|500px]] | + | |colspan="2" |'''[http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=yycI_4149667_4150509_-1 Expression at a glance]'''   {{PubMed|22383849}}<br/>[[Image:yycI_expression.png|500px|link=http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU40380]] |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 15:01, 16 May 2013
- Description: negative effector of WalK, controls cell wall metabolism
| Gene name | yycI |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | negative effector of WalK |
| Function | control of cell wall metabolism |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: yycI | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: YycI | |
| MW, pI | 32 kDa, 5.279 |
| Gene length, protein length | 840 bp, 280 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | walJ, yycH |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 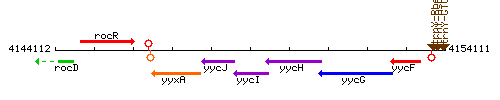
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed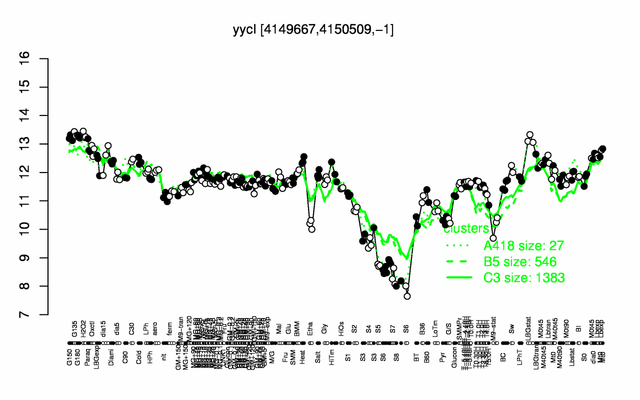
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall/ other, transcription factors and their control, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU40380
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot), spotty close to the membrane PubMed
Database entries
- UniProt: Q45612
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation: expressed during vegetative growth, repressed during stationary phase PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Tatsuya Fukushima, Isako Furihata, Robyn Emmins, Richard A Daniel, James A Hoch, Hendrik Szurmant
A role for the essential YycG sensor histidine kinase in sensing cell division.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 79(2);503-22
[PubMed:21219466]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hendrik Szurmant, Lintao Bu, Charles L Brooks, James A Hoch
An essential sensor histidine kinase controlled by transmembrane helix interactions with its auxiliary proteins.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2008, 105(15);5891-6
[PubMed:18408157]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Patrick D McLaughlin, Benjamin G Bobay, Erin J Regel, Richele J Thompson, James A Hoch, John Cavanagh
Predominantly buried residues in the response regulator Spo0F influence specific sensor kinase recognition.
FEBS Lett: 2007, 581(7);1425-9
[PubMed:17350627]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hendrik Szurmant, Michael A Mohan, P Michael Imus, James A Hoch
YycH and YycI interact to regulate the essential YycFG two-component system in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(8);3280-9
[PubMed:17307850]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Eugenio Santelli, Robert C Liddington, Michael A Mohan, James A Hoch, Hendrik Szurmant
The crystal structure of Bacillus subtilis YycI reveals a common fold for two members of an unusual class of sensor histidine kinase regulatory proteins.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(8);3290-5
[PubMed:17307848]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Fabret, J A Hoch
A two-component signal transduction system essential for growth of Bacillus subtilis: implications for anti-infective therapy.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(23);6375-83
[PubMed:9829949]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)