Difference between revisions of "YwbF"
(→This gene is a member of the following regulons) |
|||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
= This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| − | + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[AbrB regulon]]}} | |
=The gene= | =The gene= | ||
Revision as of 17:24, 8 July 2011
- Description: unknown
| Gene name | ywbF |
| Synonyms | ipa-21r |
| Essential | no |
| Product | unknown |
| Function | unknown |
| MW, pI | 43 kDa, 9.705 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1197 bp, 399 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ywbG, ywbE |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 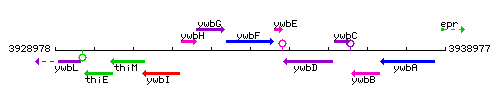
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
membrane proteins, proteins of unknown function
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU38340
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: HcaT subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39589
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Onuma Chumsakul, Hiroki Takahashi, Taku Oshima, Takahiro Hishimoto, Shigehiko Kanaya, Naotake Ogasawara, Shu Ishikawa
Genome-wide binding profiles of the Bacillus subtilis transition state regulator AbrB and its homolog Abh reveals their interactive role in transcriptional regulation.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2011, 39(2);414-28
[PubMed:20817675]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)