Difference between revisions of "YtiA"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || survival of salt stress | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || survival of salt stress | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtiexpress/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtiexpress/bsu/BSU30700 ytiA] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/startpage/start/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/interactionList/2/YtiA YtiA] | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/startpage/start/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/interactionList/2/YtiA YtiA] | ||
Revision as of 15:14, 7 August 2012
- Description: general stress protein, binds in the stationary phase to the ribosome, replaces RpmE under conditions of zinc limitation
| Gene name | ytiA |
| Synonyms | rpmE2, rpmEB |
| Essential | no |
| Product | accessory ribosomal protein |
| Function | survival of salt stress |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ytiA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: YtiA | |
| MW, pI | 9 kDa, 9.808 |
| Gene length, protein length | 246 bp, 82 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ytiB, ythA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 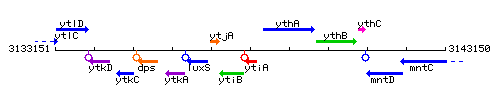
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed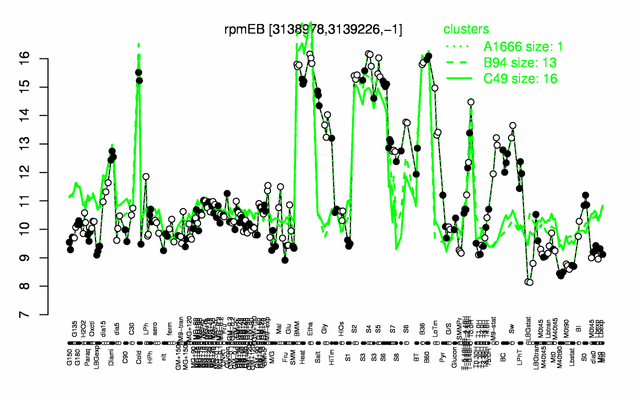
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
translation, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU30700
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: Type B subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): RpmE
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on Arg-70 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O34967
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Pierre Nicolas, Ulrike Mäder, Etienne Dervyn, Tatiana Rochat, Aurélie Leduc, Nathalie Pigeonneau, Elena Bidnenko, Elodie Marchadier, Mark Hoebeke, Stéphane Aymerich, Dörte Becher, Paola Bisicchia, Eric Botella, Olivier Delumeau, Geoff Doherty, Emma L Denham, Mark J Fogg, Vincent Fromion, Anne Goelzer, Annette Hansen, Elisabeth Härtig, Colin R Harwood, Georg Homuth, Hanne Jarmer, Matthieu Jules, Edda Klipp, Ludovic Le Chat, François Lecointe, Peter Lewis, Wolfram Liebermeister, Anika March, Ruben A T Mars, Priyanka Nannapaneni, David Noone, Susanne Pohl, Bernd Rinn, Frank Rügheimer, Praveen K Sappa, Franck Samson, Marc Schaffer, Benno Schwikowski, Leif Steil, Jörg Stülke, Thomas Wiegert, Kevin M Devine, Anthony J Wilkinson, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Michael Hecker, Uwe Völker, Philippe Bessières, Philippe Noirot
Condition-dependent transcriptome reveals high-level regulatory architecture in Bacillus subtilis.
Science: 2012, 335(6072);1103-6
[PubMed:22383849]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Scott E Gabriel, John D Helmann
Contributions of Zur-controlled ribosomal proteins to growth under zinc starvation conditions.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(19);6116-22
[PubMed:19648245]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yousuke Natori, Hideaki Nanamiya, Genki Akanuma, Saori Kosono, Toshiaki Kudo, Kozo Ochi, Fujio Kawamura
A fail-safe system for the ribosome under zinc-limiting conditions in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 63(1);294-307
[PubMed:17163968]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Genki Akanuma, Hideaki Nanamiya, Yousuke Natori, Naofumi Nomura, Fujio Kawamura
Liberation of zinc-containing L31 (RpmE) from ribosomes by its paralogous gene product, YtiA, in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(7);2715-20
[PubMed:16547061]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Dirk Höper, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
Comprehensive characterization of the contribution of individual SigB-dependent general stress genes to stress resistance of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(8);2810-26
[PubMed:15805528]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hideaki Nanamiya, Genki Akanuma, Yousuke Natori, Rikinori Murayama, Saori Kosono, Toshiaki Kudo, Kazuo Kobayashi, Naotake Ogasawara, Seung-Moon Park, Kozo Ochi, Fujio Kawamura
Zinc is a key factor in controlling alternation of two types of L31 protein in the Bacillus subtilis ribosome.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 52(1);273-83
[PubMed:15049826]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ekaterina M Panina, Andrey A Mironov, Mikhail S Gelfand
Comparative genomics of bacterial zinc regulons: enhanced ion transport, pathogenesis, and rearrangement of ribosomal proteins.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2003, 100(17);9912-7
[PubMed:12904577]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)