Difference between revisions of "YsbB"
(→Biological materials) |
|||
| Line 111: | Line 111: | ||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
| + | ** GP1554 (''ysbAB''::''spc''), available in [[Stülke]] lab | ||
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
Revision as of 09:11, 11 November 2011
- Description: putative peptidoglycan hydrolase, probably involved in cell wall turnover
| Gene name | ysbB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | unknown |
| Function | unknown |
| MW, pI | 24 kDa, 9.81 |
| Gene length, protein length | 693 bp, 231 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yscB, ysbA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 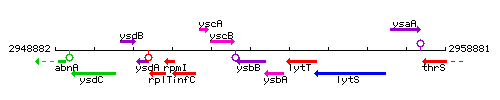
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall degradation/ turnover
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28900
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: LrgB subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P94516
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP1554 (ysbAB::spc), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
A Wipat, N Carter, S C Brignell, B J Guy, K Piper, J Sanders, P T Emmerson, C R Harwood
The dnaB-pheA (256 degrees-240 degrees) region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome containing genes responsible for stress responses, the utilization of plant cell walls and primary metabolism.
Microbiology (Reading): 1996, 142 ( Pt 11);3067-78
[PubMed:8969504]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)