Difference between revisions of "YlnE"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[biosynthesis of cofactors]]}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[CymR regulon]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[S-box]]}} | ||
=The gene= | =The gene= | ||
| Line 51: | Line 58: | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
=The protein= | =The protein= | ||
Revision as of 19:30, 8 December 2010
- Description: probable siroheme ferrochelatase
| Gene name | ylnE |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | probable siroheme ferrochelatase |
| Function | siroheme biosynthesis, sulfite reduction |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Cys, Met & Sulfate assimilation | |
| MW, pI | 28 kDa, 6.063 |
| Gene length, protein length | 783 bp, 261 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ylnD, ylnF |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 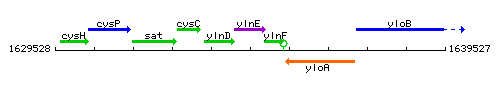
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15620
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Siroheme + 2 H+ = sirohydrochlorin + Fe2+ (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: SirB subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O34632
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- S-box: transcription termination/ antitermination, the S-box riboswitch binds S-adenosylmethionine resulting in termination PubMed
- CymR: transcription repression
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Jerneja Tomsic, Brooke A McDaniel, Frank J Grundy, Tina M Henkin
Natural variability in S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)-dependent riboswitches: S-box elements in bacillus subtilis exhibit differential sensitivity to SAM In vivo and in vitro.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(3);823-33
[PubMed:18039762]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Daniela Albanesi, Maria Cecilia Mansilla, Gustavo E Schujman, Diego de Mendoza
Bacillus subtilis cysteine synthetase is a global regulator of the expression of genes involved in sulfur assimilation.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(22);7631-8
[PubMed:16267287]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Knut Büttner, Rüdiger Bode, Michael Hecker
Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(15);4288-95
[PubMed:12107147]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M C Mansilla, D Albanesi, D de Mendoza
Transcriptional control of the sulfur-regulated cysH operon, containing genes involved in L-cysteine biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(20);5885-92
[PubMed:11004190]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)