YflT
Revision as of 11:48, 13 August 2012 by Raphael2215 (talk | contribs)
- Description: general stress protein, survival of ethanol stress
| Gene name | yflT |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | unknown |
| Function | survival of ethanol stress |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: yflT | |
| MW, pI | 12 kDa, 4.806 |
| Gene length, protein length | 345 bp, 115 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yfmA, pel |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 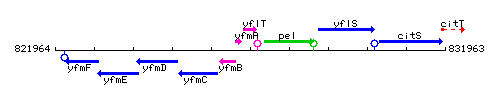
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed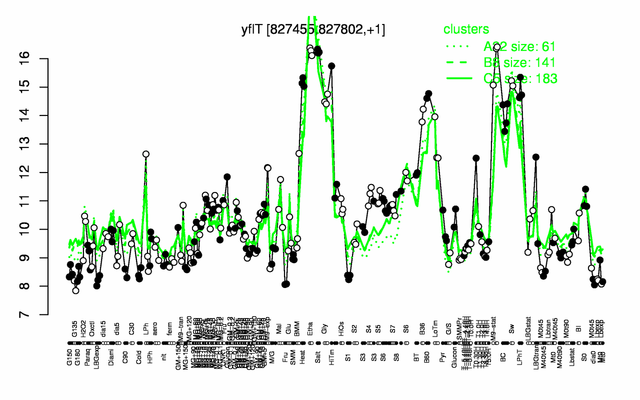
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
general stress proteins (controlled by SigB)
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU07550
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P80241
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: yflT (according to DBTBS)
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Dirk Höper, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
Comprehensive characterization of the contribution of individual SigB-dependent general stress genes to stress resistance of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(8);2810-26
[PubMed:15805528]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Knut Büttner, Rüdiger Bode, Michael Hecker
Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(15);4288-95
[PubMed:12107147]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)