Difference between revisions of "UreC"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || utilization of urea as alternative nitrogen source | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || utilization of urea as alternative nitrogen source | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/purines_catabolism.html Purine catabolism], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/glutamate.html Ammonium/ glutamate]''' | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/purines_catabolism.html Purine catabolism], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/glutamate.html Ammonium/ glutamate], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/other_nitrogen_sources/index.html Alternative nitrogen sources]''' |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 61 kDa, 5.091 | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 61 kDa, 5.091 | ||
Revision as of 10:53, 11 December 2010
- Description: urease (alpha subunit)
| Gene name | ureC |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | urease (alpha subunit) |
| Function | utilization of urea as alternative nitrogen source |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Purine catabolism, Ammonium/ glutamate, Alternative nitrogen sources | |
| MW, pI | 61 kDa, 5.091 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1707 bp, 569 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ywnA, ureB |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 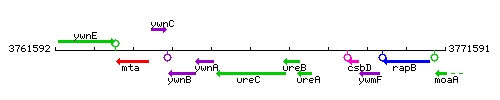
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of nitrogen sources other than amino acids
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CodY regulon, GlnR regulon, PucR regulon, SigH regulon, TnrA regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU36640
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Urea + H2O = CO2 + 2 NH3 (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: urease family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P77837
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 3.5.1.5
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Virginie Molle, Yoshiko Nakaura, Robert P Shivers, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Richard Losick, Yasutaro Fujita, Abraham L Sonenshein
Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(6);1911-22
[PubMed:12618455]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jaclyn L Brandenburg, Lewis V Wray, Lars Beier, Hanne Jarmer, Hans H Saxild, Susan H Fisher
Roles of PucR, GlnR, and TnrA in regulating expression of the Bacillus subtilis ure P3 promoter.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(21);6060-4
[PubMed:12374841]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L V Wray, A E Ferson, S H Fisher
Expression of the Bacillus subtilis ureABC operon is controlled by multiple regulatory factors including CodY, GlnR, TnrA, and Spo0H.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(17);5494-501
[PubMed:9287005]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)