Difference between revisions of "ThrS"
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
* '''Domains:''' | * '''Domains:''' | ||
| − | * '''Modification:''' | + | * '''Modification:'''Cys573 is S-bacillithiolated by NaOCl stress [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/22938038 PubMed] |
* '''Cofactor(s):''' | * '''Cofactor(s):''' | ||
| Line 143: | Line 143: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>8288542,1379177,19258532,7476165,12136084,8969504 ,17114254, 22848659</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>22938038,8288542,1379177,19258532,7476165,12136084,8969504 ,17114254, 22848659</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 08:31, 6 September 2012
- Description: threonyl-tRNA synthetase (major)
| Gene name | thrS |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | threonyl-tRNA synthetase (major) |
| Function | translation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: thrS | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: tRNA charging | |
| MW, pI | 73 kDa, 5.214 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1929 bp, 643 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ysaA, ytxC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 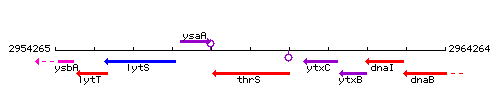
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed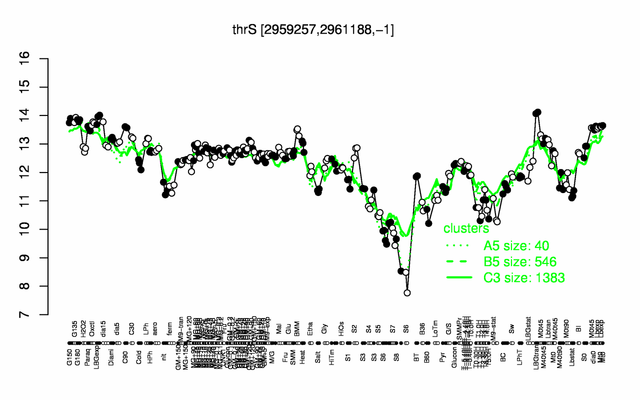
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28950
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + L-threonine + tRNA(Thr) = AMP + diphosphate + L-threonyl-tRNA(Thr) (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: class-II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:Cys573 is S-bacillithiolated by NaOCl stress PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: P18255
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 6.1.1.3
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- T-box: RNA switch, transcriptional antitermination PubMed
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Bui Khanh Chi, Alexandra A Roberts, Tran Thi Thanh Huyen, Katrin Bäsell, Dörte Becher, Dirk Albrecht, Chris J Hamilton, Haike Antelmann
S-bacillithiolation protects conserved and essential proteins against hypochlorite stress in firmicutes bacteria.
Antioxid Redox Signal: 2013, 18(11);1273-95
[PubMed:22938038]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alex Rosenberg, Lior Sinai, Yoav Smith, Sigal Ben-Yehuda
Dynamic expression of the translational machinery during Bacillus subtilis life cycle at a single cell level.
PLoS One: 2012, 7(7);e41921
[PubMed:22848659]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ana Gutiérrez-Preciado, Tina M Henkin, Frank J Grundy, Charles Yanofsky, Enrique Merino
Biochemical features and functional implications of the RNA-based T-box regulatory mechanism.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2009, 73(1);36-61
[PubMed:19258532]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Helena B Thomaides, Ella J Davison, Lisa Burston, Hazel Johnson, David R Brown, Alison C Hunt, Jeffery Errington, Lloyd Czaplewski
Essential bacterial functions encoded by gene pairs.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(2);591-602
[PubMed:17114254]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Harald Putzer, Ciarán Condon, Dominique Brechemier-Baey, Renata Brito, Marianne Grunberg-Manago
Transfer RNA-mediated antitermination in vitro.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2002, 30(14);3026-33
[PubMed:12136084]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
A Wipat, N Carter, S C Brignell, B J Guy, K Piper, J Sanders, P T Emmerson, C R Harwood
The dnaB-pheA (256 degrees-240 degrees) region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome containing genes responsible for stress responses, the utilization of plant cell walls and primary metabolism.
Microbiology (Reading): 1996, 142 ( Pt 11);3067-78
[PubMed:8969504]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Putzer, S Laalami, A A Brakhage, C Condon, M Grunberg-Manago
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase gene regulation in Bacillus subtilis: induction, repression and growth-rate regulation.
Mol Microbiol: 1995, 16(4);709-18
[PubMed:7476165]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N Gendron, H Putzer, M Grunberg-Manago
Expression of both Bacillus subtilis threonyl-tRNA synthetase genes is autogenously regulated.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(2);486-94
[PubMed:8288542]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Putzer, N Gendron, M Grunberg-Manago
Co-ordinate expression of the two threonyl-tRNA synthetase genes in Bacillus subtilis: control by transcriptional antitermination involving a conserved regulatory sequence.
EMBO J: 1992, 11(8);3117-27
[PubMed:1379177]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)