SigV
- Description: RNA polymerase ECF-type sigma factor SigV
| Gene name | sigV |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | RNA polymerase ECF-type sigma factor SigV |
| Function | response to lysozyme |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: sigV | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SigV | |
| MW, pI | 19 kDa, 9.037 |
| Gene length, protein length | 498 bp, 166 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yrhO, rsiV |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 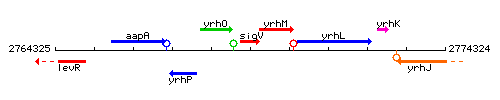
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription, sigma factors and their control, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y)
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The SigV regulon:
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU27120
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ECF subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O05404
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- Expression of the SigV regulon in increased in ugtP mutants PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Thomas Wiegert, University of Bayreuth, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Jessica L Hastie, Kyle B Williams, Craig D Ellermeier
The activity of σV, an extracytoplasmic function σ factor of Bacillus subtilis, is controlled by regulated proteolysis of the anti-σ factor RsiV.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(14);3135-44
[PubMed:23687273]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Satoshi Matsuoka, Minako Chiba, Yu Tanimura, Michihiro Hashimoto, Hiroshi Hara, Kouji Matsumoto
Abnormal morphology of Bacillus subtilis ugtP mutant cells lacking glucolipids.
Genes Genet Syst: 2011, 86(5);295-304
[PubMed:22362028]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Veronica Guariglia-Oropeza, John D Helmann
Bacillus subtilis σ(V) confers lysozyme resistance by activation of two cell wall modification pathways, peptidoglycan O-acetylation and D-alanylation of teichoic acids.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(22);6223-32
[PubMed:21926231]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Theresa D Ho, Jessica L Hastie, Peter J Intile, Craig D Ellermeier
The Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic function σ factor σ(V) is induced by lysozyme and provides resistance to lysozyme.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(22);6215-22
[PubMed:21856855]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yun Luo, Kei Asai, Yoshito Sadaie, John D Helmann
Transcriptomic and phenotypic characterization of a Bacillus subtilis strain without extracytoplasmic function σ factors.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(21);5736-45
[PubMed:20817771]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Michihiro Hashimoto, Hiroaki Takahashi, Yoshinori Hara, Hiroshi Hara, Kei Asai, Yoshito Sadaie, Kouji Matsumoto
Induction of extracytoplasmic function sigma factors in Bacillus subtilis cells with membranes of reduced phosphatidylglycerol content.
Genes Genet Syst: 2009, 84(3);191-8
[PubMed:19745567]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Thorsten Mascher, Anna-Barbara Hachmann, John D Helmann
Regulatory overlap and functional redundancy among Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic function sigma factors.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(19);6919-27
[PubMed:17675383]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Stephan Zellmeier, Claudia Hofmann, Sylvia Thomas, Thomas Wiegert, Wolfgang Schumann
Identification of sigma(V)-dependent genes of Bacillus subtilis.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2005, 253(2);221-9
[PubMed:16274938]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Mika Yoshimura, Kei Asai, Yoshito Sadaie, Hirofumi Yoshikawa
Interaction of Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors with the N-terminal regions of their potential anti-sigma factors.
Microbiology (Reading): 2004, 150(Pt 3);591-599
[PubMed:14993308]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)