Difference between revisions of "SecY"
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:secY_context.gif]] | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:secY_context.gif]] | ||
<div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | <div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan="2" |'''[http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=secY_144527_145822_1 Expression at a glance]'''   {{PubMed|22383849}}<br/>[[Image:secY_expression.png|500px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
Revision as of 13:15, 8 August 2012
- Description: preprotein translocase subunit, universally conserved protein
| Gene name | secY |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | preprotein translocase subunit |
| Function | protein secretion |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: secY | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SecY | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Protein secretion | |
| MW, pI | 47 kDa, 10.209 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1293 bp, 431 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | rplO, adk |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 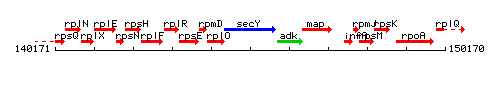
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed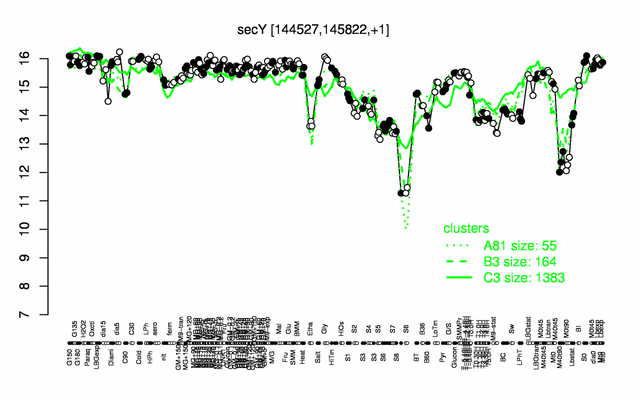
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein secretion, essential genes, membrane proteins, universally conserved proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU01360
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: secY/SEC61-alpha family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: membrane PubMed
Database entries
- UniProt: P16336
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: rplO-secY-adk-map
- Sigma factor:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: Pspac-secY PubMed
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Jochen Zimmer, Yunsun Nam, Tom A Rapoport
Structure of a complex of the ATPase SecA and the protein-translocation channel.
Nature: 2008, 455(7215);936-43
[PubMed:18923516]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
John F Hunt, Sevil Weinkauf, Lisa Henry, John J Fak, Paul McNicholas, Donald B Oliver, Johann Deisenhofer
Nucleotide control of interdomain interactions in the conformational reaction cycle of SecA.
Science: 2002, 297(5589);2018-26
[PubMed:12242434]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
J W Suh, S A Boylan, S H Oh, C W Price
Genetic and transcriptional organization of the Bacillus subtilis spc-alpha region.
Gene: 1996, 169(1);17-23
[PubMed:8635744]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R Breitling, B Schlott, D Behnke
Modulation of the spc operon affects growth and protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis.
J Basic Microbiol: 1994, 34(3);145-55
[PubMed:8071801]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J W Suh, S A Boylan, S M Thomas, K M Dolan, D B Oliver, C W Price
Isolation of a secY homologue from Bacillus subtilis: evidence for a common protein export pathway in eubacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 1990, 4(2);305-14
[PubMed:2110998]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)