SecA
- Description: preprotein translocase subunit (ATPase), required for membrane targeting of DivIVA
| Gene name | secA |
| Synonyms | div, div-341, ts-341 |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | preprotein translocase subunit (ATPase) |
| Function | protein secretion |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: secA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SecA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: SecA | |
| MW, pI | 95 kDa, 5.34 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2523 bp, 841 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | prfB, yvyD |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 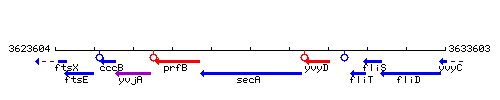
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed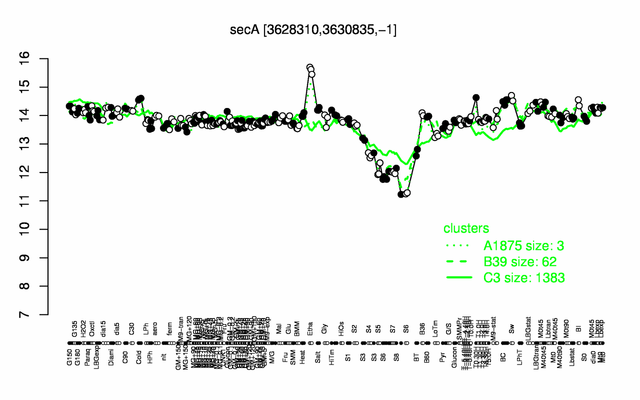
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein secretion, essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35300
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35300
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: SecA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): none in Bacillus, some species have a paralogous secA gene named secA2 that has an altered substrate range
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: nucleotide binding domain, preprotein binding domain, IRA2 domain, scaffold domain, wing domain, IRA1 domain, C-terminal domain
- Modification:
- Cofactors: Mg
- Effectors of protein activity: anionic phospholipids, preprotein, SecY, signal peptides (even when added in trans) PubMed
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35300
- UniProt: P28366
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 945 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2829 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 411 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 395 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 564 PubMed
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Sven Halbedel, Maki Kawai, Reinhard Breitling, Leendert W Hamoen
SecA is required for membrane targeting of the cell division protein DivIVA in vivo.
Front Microbiol: 2014, 5;58
[PubMed:24592260]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P e)
Chun-Kai Yang, Chung-Dar Lu, Phang C Tai
Differential expression of secretion machinery during bacterial growth: SecY and SecF decrease while SecA increases during transition from exponential phase to stationary phase.
Curr Microbiol: 2013, 67(6);682-7
[PubMed:23852076]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jianmei Cui, Jinshan Jin, Ying-Hsin Hsieh, Hsiuchin Yang, Bowen Ke, Krishna Damera, Phang C Tai, Binghe Wang
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of rose bengal analogues as SecA inhibitors.
ChemMedChem: 2013, 8(8);1384-93
[PubMed:23794293]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sarah M Auclair, Donald B Oliver, Ishita Mukerji
Defining the solution state dimer structure of Escherichia coli SecA using Förster resonance energy transfer.
Biochemistry: 2013, 52(14);2388-401
[PubMed:23484952]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Dorothy M Kim, Haiyan Zheng, Yuanpeng J Huang, Gaetano T Montelione, John F Hunt
ATPase active-site electrostatic interactions control the global conformation of the 100 kDa SecA translocase.
J Am Chem Soc: 2013, 135(8);2999-3010
[PubMed:23167435]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hiroshi Kakeshita, Yasushi Kageyama, Katsutoshi Ara, Katsuya Ozaki, Kouji Nakamura
Enhanced extracellular production of heterologous proteins in Bacillus subtilis by deleting the C-terminal region of the SecA secretory machinery.
Mol Biotechnol: 2010, 46(3);250-7
[PubMed:20574771]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Benedikt W Bauer, Tom A Rapoport
Mapping polypeptide interactions of the SecA ATPase during translocation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2009, 106(49);20800-5
[PubMed:19933328]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Giorgos Gouridis, Spyridoula Karamanou, Ioannis Gelis, Charalampos G Kalodimos, Anastassios Economou
Signal peptides are allosteric activators of the protein translocase.
Nature: 2009, 462(7271);363-7
[PubMed:19924216]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jochen Zimmer, Tom A Rapoport
Conformational flexibility and peptide interaction of the translocation ATPase SecA.
J Mol Biol: 2009, 394(4);606-12
[PubMed:19850053]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jochen Zimmer, Yunsun Nam, Tom A Rapoport
Structure of a complex of the ATPase SecA and the protein-translocation channel.
Nature: 2008, 455(7215);936-43
[PubMed:18923516]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ulf Gerth, Holger Kock, Ilja Kusters, Stephan Michalik, Robert L Switzer, Michael Hecker
Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(1);321-31
[PubMed:17981983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Haiyuan Ding, John F Hunt, Ishita Mukerji, Donald Oliver
Bacillus subtilis SecA ATPase exists as an antiparallel dimer in solution.
Biochemistry: 2003, 42(29);8729-38
[PubMed:12873133]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
John F Hunt, Sevil Weinkauf, Lisa Henry, John J Fak, Paul McNicholas, Donald B Oliver, Johann Deisenhofer
Nucleotide control of interdomain interactions in the conformational reaction cycle of SecA.
Science: 2002, 297(5589);2018-26
[PubMed:12242434]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jan D H Jongbloed, Haike Antelmann, Michael Hecker, Reindert Nijland, Sierd Bron, Ulla Airaksinen, Frens Pries, Wim J Quax, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Peter G Braun
Selective contribution of the twin-arginine translocation pathway to protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis.
J Biol Chem: 2002, 277(46);44068-78
[PubMed:12218047]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J P Müller, J Ozegowski, S Vettermann, J Swaving, K H Van Wely, A J Driessen
Interaction of Bacillus subtilis CsaA with SecA and precursor proteins.
Biochem J: 2000, 348 Pt 2(Pt 2);367-73
[PubMed:10816431]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
M Herbort, M Klein, E H Manting, A J Driessen, R Freudl
Temporal expression of the Bacillus subtilis secA gene, encoding a central component of the preprotein translocase.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(2);493-500
[PubMed:9882663]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Bunai, K Yamada, K Hayashi, K Nakamura, K Yamane
Enhancing effect of Bacillus subtilis Ffh, a homologue of the SRP54 subunit of the mammalian signal recognition particle, on the binding of SecA to precursors of secretory proteins in vitro.
J Biochem: 1999, 125(1);151-9
[PubMed:9880811]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Takamatsu, S Fuma, K Nakamura, Y Sadaie, A Shinkai, S Matsuyama, S Mizushima, K Yamane
In vivo and in vitro characterization of the secA gene product of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(13);4308-16
[PubMed:1385592]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)