Difference between revisions of "Sandbox"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' catabolic | + | * '''Description:''' Carbon catabolite control protein A, involved in glucose regulation of many genes; represses catabolic genes and activates genes involved in excretion of excess carbon <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Gene name''' | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Gene name''' | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''ccpA'' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Synonyms''' || '' '' | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Synonyms''' || ''graR, alsA, amyR'' |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || transcriptional regulator |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || mediates carbon catabolite repression (CCR) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 36,8 kDa, 5.06 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || 1002 bp, 334 amino acids |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[ | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[aroA]]'', ''[[motP]]'' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/ | + | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/ccpA_nucleotide.txt Gene sequence (+200bp) ]''' |
| − | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/ | + | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/ccpA_protein.txt Protein sequence]''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image: | + | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:ccpA_context.gif]] |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
=== Basic information === | === Basic information === | ||
| − | * '''Coordinates:''' | + | * '''Coordinates:''' 3043210 - 3044211 |
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
| − | + | Loss of carbon catabolite repression. | |
| + | Loss of PTS-dependent sugar transport due to excessive phosphorylation of [[PtsH |HPr]] by [[HprK]]. | ||
| + | The mutant is unable to grow on a minimal medium with glucose and ammonium as the only sources of carbon and nitrogen, respectively. | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/ | + | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/ccpA-motPS.html] |
| − | * '''SubtiList entry:''' [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/genome.cgi?gene_detail+ | + | * '''SubtiList entry:''' [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/genome.cgi?gene_detail+BG10376] |
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| Line 54: | Line 56: | ||
=== Basic information/ Evolution === | === Basic information/ Evolution === | ||
| − | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' | + | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' transcriptional regulator of carbon catabolite repression (CCR) |
| − | * '''Protein family:''' | + | * '''Protein family:''' LacI family |
| − | * '''Paralogous protein(s):''' | + | * '''Paralogous protein(s):''' |
=== Extended information on the protein === | === Extended information on the protein === | ||
| Line 65: | Line 67: | ||
* '''Domains:''' | * '''Domains:''' | ||
| + | ** HTH lacI-type Domain (1 – 58) | ||
| + | ** DNA binding Domain (6 – 25) | ||
* '''Modification:''' | * '''Modification:''' | ||
| − | * '''Cofactor(s):''' | + | * '''Cofactor(s):''' [[PtsH |HPr]]-Ser46-P, Crh-Ser-46-P |
| − | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | + | * '''Effectors of protein activity:'''glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17376479?ordinalpos=1&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_DefaultReportPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum Pubmed] |
| − | * '''Interactions:''' | + | * '''Interactions:''' CcpA-[[PtsH |HPr]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15369672?ordinalpos=3&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_DefaultReportPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum PubMed], CcpA-[[Crh]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16316990?ordinalpos=2&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_DefaultReportPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum PubMed] |
* '''Localization:''' | * '''Localization:''' | ||
| Line 78: | Line 82: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''Structure:''' | + | * '''Structure:''' CcpA-Crh-DNA-complex [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?Dopt=s&uid=52326 NCBI], complex with P-Ser-[[PtsH |HPr]] and sulphate ions [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?Dopt=s&uid=39857 NCBI] |
| − | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www. | + | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.expasy.ch/cgi-bin/sprot-search-ac?P25144] |
| − | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu: | + | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu:BSU29740] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | |||
=Expression and regulation= | =Expression and regulation= | ||
| − | * '''Operon:''' '' | + | * '''Operon:''' ''[[ccpA]] [[motP]] [[motS]]'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16547058 PubMed] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''Sigma factor:''' |
| − | * ''' | + | * '''Regulation:''' constitutively expressed [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/18757537 PubMed] |
| − | * '''Additional information:''' | + | * '''Additional information:''' there are about 3.000 molecules of CcpA per cell [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8000527 PubMed] |
| − | |||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' | + | * '''Mutant:''' QB5407 (spc), GP302 (erm), GP300 (an in frame deletion of ccpA), available in [[Stülke]] lab |
| − | * '''Expression vector:''' | + | * '''Expression vector:''' pGP643 (in [[pGP380]], for SPINE, expression in Bacillus subtilis) |
* '''lacZ fusion:''' | * '''lacZ fusion:''' | ||
| Line 112: | Line 110: | ||
* '''GFP fusion:''' | * '''GFP fusion:''' | ||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''Antibody:''' available in [[Hillen]] and [[Stülke]] labs |
| + | |||
| + | =Labs working on this gene/protein= | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Wolfgang Hillen]], Erlangen University, Germany [http://www.biologie.uni-erlangen.de/mibi/index2.html Homepage] | ||
| − | + | [[Richard Brennan]], Houston, Texas, USA [http://www.mdanderson.org/departments/biochem/display.cfm?id=556ef368-6c81-4043-b74f350d41dd06cb&method=displayfull&pn=a8427ebd-d0ff-11d4-80fd00508b603a14 Homepage] | |
| − | + | [[Milton H. Saier]], University of California at San Diego, USA [http://biology.ucsd.edu/faculty/saier.html Homepage] | |
| − | [[ | + | [[Yasutaro Fujita]], University of Fukuyama, Japan |
| − | [[Stülke|Jörg Stülke]], University of Göttingen, Germany | + | [[Stülke|Jörg Stülke]], University of Göttingen, Germany [http://wwwuser.gwdg.de/~genmibio/stuelke.html Homepage] |
| − | [http://wwwuser.gwdg.de/~genmibio/stuelke.html Homepage] | ||
=Your additional remarks= | =Your additional remarks= | ||
| Line 127: | Line 128: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | # | + | '''Reviews''' |
| − | # | + | |
| − | # | + | # Henkin, T. M. (1996) The role of the CcpA transcriptional regulator in carbon metabolism in Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 135: 9-15. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8598282 PubMed] |
| − | # | + | # Warner, J. B. & Lolkema, J. S. CcpA-dependent carbon catabolite repression in bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 67, 475-490 (2003). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/14665673 PubMed] |
| − | # | + | |
| − | # | + | '''General and physiological studies''' |
| − | # | + | |
| − | # Belitsky BR, Sonenshein, AL: CcpA-dependent regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamate dehydrogenase gene expression. J Bacteriol 2004, 186:3392-3398. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/ | + | # Henkin, T. M., Grundy, F. J., Nicholson, W. L. and Chambliss, G. H. (1991) Catabolite repression of -amylase gene expression in Bacillus subtilis involves a trans-acting gene product homologous to the Escherichia coli lacI and galR repressors. Mol. Microbiol. 5, 575-584. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/1904524 PubMed] |
| − | # | + | # Faires, N., Tobisch, S., Bachem, S., Martin-Verstraete, I., Hecker, M., & Stülke, J. (1999) The catabolite control protein CcpA controls ammonium assimilation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1: 141-148. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10941796 PubMed] |
| − | # | + | # Ludwig, H., Rebhan, N., Blencke, H.-M., Merzbacher, M. & Stülke, J. (2002) Control of the glycolytic gapA operon by the catabolite control protein A in Bacillus subtilis: a novel mechanism of CcpA-mediated regulation. Mol. Microbiol. 45: 543-553. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12123463 PubMed] |
| − | # | + | # Miwa, Y., M. Saikawa, and Y. Fujita. 1994. Possible function and some properties of the CcpA protein of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 140:2567-2575. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8000527 PubMed] |
| + | # Singh, K. D., Schmalisch, M. H., Stülke, J. & Görke, B. (2008) Carbon catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis: A quantitative analysis of repression exerted by different carbon sources. J. Bacteriol. 190: 7275-7284. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/18757537 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Terahara et al. (2006) An intergenic stem-loop mutation in the Bacillus subtilis ccpA-motPS operon increases motPS transcription and the MotPS contribution to motility ''J Bacteriol.'' '''188:''' 2701-2705. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16547058 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Wacker, I., Ludwig, H., Reif, I., Blencke, H.-M., Detsch, C. & Stülke, J. (2003) The regulatory link between carbon and nitrogen metabolism in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the gltAB operon by the catabolite control protein CcpA. Microbiology 149: 3001-3009. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/14523131 PubMed] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Global analyses (proteome, transcriptome)''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Blencke, H.-M., Homuth, G., Ludwig, H., Mäder, U., Hecker, M. & Stülke, J. (2003) Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways. Metab. Engn. 5: 133-149. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12850135 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Moreno MS, Schneider BL, Maile RR, Weyler W, Saier Jr MH: Catabolite repression mediated by CcpA protein in Bacillus subtilis: novel modes of regulation revealed by whole-genome analysis. Mol Microbiol 2001, 39:1366-1381. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/11251851 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Tobisch, S., Zühlke, D., Bernhardt, J., Stülke, J. & Hecker, M. (1999) Role of CcpA in regulation of the central pathways of carbon catabolism in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 181: 6996-7004. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10559165 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Yoshida, K.-I., Kobayashi, K., Miwa, Y., Kang, C.-M., Matsunaga, M., Yamaguchi, H., Tojo, S., Yamamoto, M., Nishi, R., Ogasawara, N., Nakayama, T. & Fujita, Y. (2001). Combined transcriptome and proteome analysis as a powerful approach to study genes under glucose repression in Bacillus subtilis. Nucl Acids Res 29, 6683-6692. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/11160890 PubMed] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Repression of target genes by CcpA''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Belitsky BR, Sonenshein, AL: CcpA-dependent regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamate dehydrogenase gene expression. J Bacteriol 2004, 186:3392-3398. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15150224 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Choi SK, Saier MH Jr: Regulation of sigL expression by the catabolite control protein CcpA involves a roadblock mechanism in Bacillus subtilis: potential connection between carbon and nitrogen metabolism. J Bacteriol 2005, 187:6856-6861. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16166551 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Darbon, E., Servant, P., Poncet, S., and Deutscher, J. (2002). Antitermination by GlpP, catabolite repression via CcpA and inducer exclusion triggered by P~GlpK dephosphorylation control Bacillus subtilis glpFK expression. Mol. Microbiol. 43, 1039-1052. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/11929549 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Grundy, F. J., Turinski, A. J., and Henkin, T. M. (1994). Catabolite regulation of Bacillus subtilis acetate and acetoin utilization genes by CcpA. J. Bacteriol. 176, 4527-4533. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7913927 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Inacio, J. M. & de Sá-Nogueira, I. trans-Acting factors and cis-elements involved in glucose repression of arabinan degradation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 189, 8371-8376 (2007). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/17827291 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Kim HJ, Jourlin-Castelli C, Kim SI, Sonenshein AL (2002) Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis ccpC gene by CcpA and CcpC. Mol Microbiol 43:399-410 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/11985717 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Kim HJ, Roux A, Sonenshein AL (2002) Direct and indirect roles of CcpA in regulation of Bacillus subtilis Krebs cycle genes. Mol Microbiol 45:179-190 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12100558 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Martin-Verstraete, I., Stülke, J., Klier, A. & Rapoport, G. (1995) Two different mechanisms mediate catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis levanase operon. J. Bacteriol. 177: 6919-6927. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7592486 PubMed] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Positive regulation of gene expression by CcpA''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Grundy FJ, Waters DA, Allen SH, Henkin TM (1993) Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis acetate kinase gene by CcpA. J Bacteriol 175:7348-7355 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8226682 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Ludwig, H., Meinken, C., Matin, A. & Stülke, J. (2002) Insufficient expression of the ilv-leu operon encoding enzymes of branched-chain amino acids biosynthesis limits growth of a Bacillus subtilis ccpA mutant. J. Bacteriol. 184: 5174-5178. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12193635 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Presecan-Siedel, E., Galinier, A., Longin, R., Deutscher, J., Danchin, A., Glaser, P. and Martin-Verstraete, I. (1999) The catabolite regulation of the pta gene as part of carbon flow pathways in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 181, 6889-6897. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10559153 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Shivers, R. P., and Sonenshein, A. L. (2005) Bacillus subtilis ilvB operon: an intersection of global regulons. Mol Microbiol 56: 1549-1559. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15916605 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Turinsky, A. J., Grundy, F. J., Kim, J. H., Chambliss, G. H., and Henkin, T. M. 1998. Transcriptional activation of the Bacillus subtilis ackA gene requires sequences upstream of the promoter. J. Bacteriol. 180: 5961-5967. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9811655 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Turinsky, A. J., Moir-Blais, T. R., Grundy, F. J., and Henkin, T. M. 2000. Bacillus subtilis ccpA gene mutants specifically defective in activation of acetoin synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 182:5611-5614. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10986270 PubMed] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Control of CcpA activity''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Deutscher, J., Küster, E., Bergstedt, U., Charrier, V., and Hillen, W. 1995. Protein kinase-dependent HPr/CcpA interaction links glycolytic activity to carbon catabolite repression in Gram-positive bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 15: 1049-1053. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7623661 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Galinier A, Deutscher J, Martin-Verstraete I: Phosphorylation of either Crh or HPr mediates binding of CcpA to the Bacillus subtilis xyn cre and catabolite repression of the xyn operon. J Mol Biol 1999, 286:307-314. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9973552 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Jones, B. E., Dossonnet, V., Küster, E., Hillen, W., Deutscher, J. & Klevit, R. E. (1997). Binding of the catabolite repressor protein CcpA to its DNA target is regulated by phosphorylation of its corepressor HPr. J Biol Chem 272, 26530-26535. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9334231 PubMed] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''CcpA-DNA interaction''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Fujita, Y., Miwa, Y., Galinier, A. and Deutscher, J. (1995) Specific recognition of the Bacillus subtilis gnt cis-acting catabolite-responsive element by a protein complex formed between CcpA and seryl-phosphorylated HPr. Mol. Microbiol. 17, 953-960. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8596444 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Miwa, Y., Nakata, A., Ogiwara, A., Yamamota, M., and Fujita, Y. 2000. Evaluation and characterization of catabolite-responsive elements (cre) of Bacillus subtilis. Nucl. Acids Res. 28: 1206-1210. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10666464 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Seidel G, Diel M, Fuchsbauer N, Hillen W: Quantitative interdependence of coeffectors, CcpA and cre in carbon catabolite regulation of Bacillus subtilis. FEBS J 2005, 272:2566-2577. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15885105 PubMed] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Functional analysis of CcpA''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Küster, E., Hilbich, T., Dahl, M. and Hillen, W. (1999) Mutations in catabolite control protein CcpA separating growth effects from catabolite repression. J. Bacteriol. 181, 4125-4128. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10383986 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Küster-Schöck, E., Wagner, A., Völker, U., and Hillen, W. (1999) Mutations in catabolite control protein CcpA showing glucose-independent regulation in Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol 181: 7634-7638. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10601226 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Ludwig, H. & Stülke, J. (2001) The Bacillus subtilis catabolite control protein CcpA exerts all its regulatory functions by DNA binding. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 203: 125-129. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/11557150 PubMed] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Structural analyses''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Schumacher, M. A. et al. Structural basis for allosteric control of the transcription regulator CcpA by the phosphoprotein HPr-Ser46-P. Cell 118, 731-741 (2004). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15369672 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Schumacher, M. A., Seidel, G., Hillen, W. & Brennan, R. G. Phosphoprotein Crh-Ser46-P displays altered binding to CcpA to effect carbon catabolite regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 6793-6800 (2006). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16316990 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Schumacher, M. A., Seidel, G., Hillen, W. & Brennan, R. G. Structural mechanism for the fine-tuning of CcpA function by the small molecule effectors glucose 6-phosphate and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. J. Mol. Biol. 368, 1042-1050 (2007). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/17376479 PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 16:19, 2 February 2009
- Description: Carbon catabolite control protein A, involved in glucose regulation of many genes; represses catabolic genes and activates genes involved in excretion of excess carbon
| Gene name | ccpA |
| Synonyms | graR, alsA, amyR |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator |
| Function | mediates carbon catabolite repression (CCR) |
| MW, pI | 36,8 kDa, 5.06 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1002 bp, 334 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | aroA, motP |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 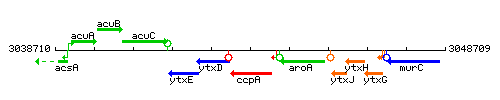
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates: 3043210 - 3044211
Phenotypes of a mutant
Loss of carbon catabolite repression. Loss of PTS-dependent sugar transport due to excessive phosphorylation of HPr by HprK. The mutant is unable to grow on a minimal medium with glucose and ammonium as the only sources of carbon and nitrogen, respectively.
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: transcriptional regulator of carbon catabolite repression (CCR)
- Protein family: LacI family
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- HTH lacI-type Domain (1 – 58)
- DNA binding Domain (6 – 25)
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): HPr-Ser46-P, Crh-Ser-46-P
- Effectors of protein activity:glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate Pubmed
- Localization:
Database entries
- Swiss prot entry: [3]
- KEGG entry: [4]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation: constitutively expressed PubMed
- Additional information: there are about 3.000 molecules of CcpA per cell PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: QB5407 (spc), GP302 (erm), GP300 (an in frame deletion of ccpA), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector: pGP643 (in pGP380, for SPINE, expression in Bacillus subtilis)
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Wolfgang Hillen, Erlangen University, Germany Homepage
Richard Brennan, Houston, Texas, USA Homepage
Milton H. Saier, University of California at San Diego, USA Homepage
Yasutaro Fujita, University of Fukuyama, Japan
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
- Henkin, T. M. (1996) The role of the CcpA transcriptional regulator in carbon metabolism in Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 135: 9-15. PubMed
- Warner, J. B. & Lolkema, J. S. CcpA-dependent carbon catabolite repression in bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 67, 475-490 (2003). PubMed
General and physiological studies
- Henkin, T. M., Grundy, F. J., Nicholson, W. L. and Chambliss, G. H. (1991) Catabolite repression of -amylase gene expression in Bacillus subtilis involves a trans-acting gene product homologous to the Escherichia coli lacI and galR repressors. Mol. Microbiol. 5, 575-584. PubMed
- Faires, N., Tobisch, S., Bachem, S., Martin-Verstraete, I., Hecker, M., & Stülke, J. (1999) The catabolite control protein CcpA controls ammonium assimilation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1: 141-148. PubMed
- Ludwig, H., Rebhan, N., Blencke, H.-M., Merzbacher, M. & Stülke, J. (2002) Control of the glycolytic gapA operon by the catabolite control protein A in Bacillus subtilis: a novel mechanism of CcpA-mediated regulation. Mol. Microbiol. 45: 543-553. PubMed
- Miwa, Y., M. Saikawa, and Y. Fujita. 1994. Possible function and some properties of the CcpA protein of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 140:2567-2575. PubMed
- Singh, K. D., Schmalisch, M. H., Stülke, J. & Görke, B. (2008) Carbon catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis: A quantitative analysis of repression exerted by different carbon sources. J. Bacteriol. 190: 7275-7284. PubMed
- Terahara et al. (2006) An intergenic stem-loop mutation in the Bacillus subtilis ccpA-motPS operon increases motPS transcription and the MotPS contribution to motility J Bacteriol. 188: 2701-2705. PubMed
- Wacker, I., Ludwig, H., Reif, I., Blencke, H.-M., Detsch, C. & Stülke, J. (2003) The regulatory link between carbon and nitrogen metabolism in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the gltAB operon by the catabolite control protein CcpA. Microbiology 149: 3001-3009. PubMed
Global analyses (proteome, transcriptome)
- Blencke, H.-M., Homuth, G., Ludwig, H., Mäder, U., Hecker, M. & Stülke, J. (2003) Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways. Metab. Engn. 5: 133-149. PubMed
- Moreno MS, Schneider BL, Maile RR, Weyler W, Saier Jr MH: Catabolite repression mediated by CcpA protein in Bacillus subtilis: novel modes of regulation revealed by whole-genome analysis. Mol Microbiol 2001, 39:1366-1381. PubMed
- Tobisch, S., Zühlke, D., Bernhardt, J., Stülke, J. & Hecker, M. (1999) Role of CcpA in regulation of the central pathways of carbon catabolism in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 181: 6996-7004. PubMed
- Yoshida, K.-I., Kobayashi, K., Miwa, Y., Kang, C.-M., Matsunaga, M., Yamaguchi, H., Tojo, S., Yamamoto, M., Nishi, R., Ogasawara, N., Nakayama, T. & Fujita, Y. (2001). Combined transcriptome and proteome analysis as a powerful approach to study genes under glucose repression in Bacillus subtilis. Nucl Acids Res 29, 6683-6692. PubMed
Repression of target genes by CcpA
- Belitsky BR, Sonenshein, AL: CcpA-dependent regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamate dehydrogenase gene expression. J Bacteriol 2004, 186:3392-3398. PubMed
- Choi SK, Saier MH Jr: Regulation of sigL expression by the catabolite control protein CcpA involves a roadblock mechanism in Bacillus subtilis: potential connection between carbon and nitrogen metabolism. J Bacteriol 2005, 187:6856-6861. PubMed
- Darbon, E., Servant, P., Poncet, S., and Deutscher, J. (2002). Antitermination by GlpP, catabolite repression via CcpA and inducer exclusion triggered by P~GlpK dephosphorylation control Bacillus subtilis glpFK expression. Mol. Microbiol. 43, 1039-1052. PubMed
- Grundy, F. J., Turinski, A. J., and Henkin, T. M. (1994). Catabolite regulation of Bacillus subtilis acetate and acetoin utilization genes by CcpA. J. Bacteriol. 176, 4527-4533. PubMed
- Inacio, J. M. & de Sá-Nogueira, I. trans-Acting factors and cis-elements involved in glucose repression of arabinan degradation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 189, 8371-8376 (2007). PubMed
- Kim HJ, Jourlin-Castelli C, Kim SI, Sonenshein AL (2002) Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis ccpC gene by CcpA and CcpC. Mol Microbiol 43:399-410 PubMed
- Kim HJ, Roux A, Sonenshein AL (2002) Direct and indirect roles of CcpA in regulation of Bacillus subtilis Krebs cycle genes. Mol Microbiol 45:179-190 PubMed
- Martin-Verstraete, I., Stülke, J., Klier, A. & Rapoport, G. (1995) Two different mechanisms mediate catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis levanase operon. J. Bacteriol. 177: 6919-6927. PubMed
Positive regulation of gene expression by CcpA
- Grundy FJ, Waters DA, Allen SH, Henkin TM (1993) Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis acetate kinase gene by CcpA. J Bacteriol 175:7348-7355 PubMed
- Ludwig, H., Meinken, C., Matin, A. & Stülke, J. (2002) Insufficient expression of the ilv-leu operon encoding enzymes of branched-chain amino acids biosynthesis limits growth of a Bacillus subtilis ccpA mutant. J. Bacteriol. 184: 5174-5178. PubMed
- Presecan-Siedel, E., Galinier, A., Longin, R., Deutscher, J., Danchin, A., Glaser, P. and Martin-Verstraete, I. (1999) The catabolite regulation of the pta gene as part of carbon flow pathways in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 181, 6889-6897. PubMed
- Shivers, R. P., and Sonenshein, A. L. (2005) Bacillus subtilis ilvB operon: an intersection of global regulons. Mol Microbiol 56: 1549-1559. PubMed
- Turinsky, A. J., Grundy, F. J., Kim, J. H., Chambliss, G. H., and Henkin, T. M. 1998. Transcriptional activation of the Bacillus subtilis ackA gene requires sequences upstream of the promoter. J. Bacteriol. 180: 5961-5967. PubMed
- Turinsky, A. J., Moir-Blais, T. R., Grundy, F. J., and Henkin, T. M. 2000. Bacillus subtilis ccpA gene mutants specifically defective in activation of acetoin synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 182:5611-5614. PubMed
Control of CcpA activity
- Deutscher, J., Küster, E., Bergstedt, U., Charrier, V., and Hillen, W. 1995. Protein kinase-dependent HPr/CcpA interaction links glycolytic activity to carbon catabolite repression in Gram-positive bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 15: 1049-1053. PubMed
- Galinier A, Deutscher J, Martin-Verstraete I: Phosphorylation of either Crh or HPr mediates binding of CcpA to the Bacillus subtilis xyn cre and catabolite repression of the xyn operon. J Mol Biol 1999, 286:307-314. PubMed
- Jones, B. E., Dossonnet, V., Küster, E., Hillen, W., Deutscher, J. & Klevit, R. E. (1997). Binding of the catabolite repressor protein CcpA to its DNA target is regulated by phosphorylation of its corepressor HPr. J Biol Chem 272, 26530-26535. PubMed
CcpA-DNA interaction
- Fujita, Y., Miwa, Y., Galinier, A. and Deutscher, J. (1995) Specific recognition of the Bacillus subtilis gnt cis-acting catabolite-responsive element by a protein complex formed between CcpA and seryl-phosphorylated HPr. Mol. Microbiol. 17, 953-960. PubMed
- Miwa, Y., Nakata, A., Ogiwara, A., Yamamota, M., and Fujita, Y. 2000. Evaluation and characterization of catabolite-responsive elements (cre) of Bacillus subtilis. Nucl. Acids Res. 28: 1206-1210. PubMed
- Seidel G, Diel M, Fuchsbauer N, Hillen W: Quantitative interdependence of coeffectors, CcpA and cre in carbon catabolite regulation of Bacillus subtilis. FEBS J 2005, 272:2566-2577. PubMed
Functional analysis of CcpA
- Küster, E., Hilbich, T., Dahl, M. and Hillen, W. (1999) Mutations in catabolite control protein CcpA separating growth effects from catabolite repression. J. Bacteriol. 181, 4125-4128. PubMed
- Küster-Schöck, E., Wagner, A., Völker, U., and Hillen, W. (1999) Mutations in catabolite control protein CcpA showing glucose-independent regulation in Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol 181: 7634-7638. PubMed
- Ludwig, H. & Stülke, J. (2001) The Bacillus subtilis catabolite control protein CcpA exerts all its regulatory functions by DNA binding. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 203: 125-129. PubMed
Structural analyses
- Schumacher, M. A. et al. Structural basis for allosteric control of the transcription regulator CcpA by the phosphoprotein HPr-Ser46-P. Cell 118, 731-741 (2004). PubMed
- Schumacher, M. A., Seidel, G., Hillen, W. & Brennan, R. G. Phosphoprotein Crh-Ser46-P displays altered binding to CcpA to effect carbon catabolite regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 6793-6800 (2006). PubMed
- Schumacher, M. A., Seidel, G., Hillen, W. & Brennan, R. G. Structural mechanism for the fine-tuning of CcpA function by the small molecule effectors glucose 6-phosphate and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. J. Mol. Biol. 368, 1042-1050 (2007). PubMed