Difference between revisions of "RpmI"
(→Additional information) |
|||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | * the protein is significantly underrepresented in 45S assembly intermediates that accumulate upon depletion of [[RbgA]] {{PubMed|23700310}} | + | * the protein is significantly underrepresented in 45S assembly intermediates that accumulate upon depletion of [[RbgA]] {{PubMed|24335279,23700310}} |
=Expression and regulation= | =Expression and regulation= | ||
Revision as of 17:26, 18 December 2013
- Description: ribosomal protein
| Gene name | rpmI |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no PubMed |
| Product | ribosomal protein L35 |
| Function | translation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rpmI | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RpmI | |
| MW, pI | 7 kDa, 12.525 |
| Gene length, protein length | 198 bp, 66 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | rplT, infC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 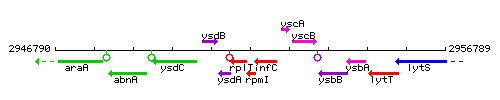
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
RplT regulon, stringent response
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28860
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ribosomal protein L35P family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P55874
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- the protein is significantly underrepresented in 45S assembly intermediates that accumulate upon depletion of RbgA PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- binding of RplT to a RNA switch in the infC leader region causes transcription termination PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Ahmad Jomaa, Nikhil Jain, Joseph H Davis, James R Williamson, Robert A Britton, Joaquin Ortega
Functional domains of the 50S subunit mature late in the assembly process.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2014, 42(5);3419-35
[PubMed:24335279]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ningning Li, Yuling Chen, Qiang Guo, Yixiao Zhang, Yi Yuan, Chengying Ma, Haiteng Deng, Jianlin Lei, Ning Gao
Cryo-EM structures of the late-stage assembly intermediates of the bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2013, 41(14);7073-83
[PubMed:23700310]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Genki Akanuma, Hideaki Nanamiya, Yousuke Natori, Koichi Yano, Shota Suzuki, Shuya Omata, Morio Ishizuka, Yasuhiko Sekine, Fujio Kawamura
Inactivation of ribosomal protein genes in Bacillus subtilis reveals importance of each ribosomal protein for cell proliferation and cell differentiation.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(22);6282-91
[PubMed:23002217]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Patrice Bruscella, Karen Shahbabian, Soumaya Laalami, Harald Putzer
RNase Y is responsible for uncoupling the expression of translation factor IF3 from that of the ribosomal proteins L35 and L20 in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 81(6);1526-41
[PubMed:21843271]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Matthew A Lauber, William E Running, James P Reilly
B. subtilis ribosomal proteins: structural homology and post-translational modifications.
J Proteome Res: 2009, 8(9);4193-206
[PubMed:19653700]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Nasslie Choonee, Sergine Even, Lena Zig, Harald Putzer
Ribosomal protein L20 controls expression of the Bacillus subtilis infC operon via a transcription attenuation mechanism.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2007, 35(5);1578-88
[PubMed:17289755]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Eymann, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Michael Hecker
Bacillus subtilis functional genomics: global characterization of the stringent response by proteome and transcriptome analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(9);2500-20
[PubMed:11948165]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)