RpmA
Revision as of 14:09, 16 May 2013 by 134.76.70.252 (talk)
- Description: ribosomal protein
| Gene name | rpmA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | ribosomal protein L27 (BL24) |
| Function | translation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rpmA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RpmA | |
| MW, pI | 10 kDa, 10.764 |
| Gene length, protein length | 282 bp, 94 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | spo0B, ysxB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 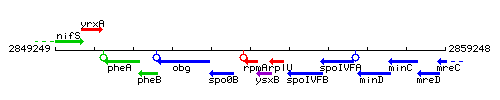
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU27940
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ribosomal protein L27P family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P05657
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: rpmA PubMed
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Matthew A Lauber, William E Running, James P Reilly
B. subtilis ribosomal proteins: structural homology and post-translational modifications.
J Proteome Res: 2009, 8(9);4193-206
[PubMed:19653700]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Wipat, N Carter, S C Brignell, B J Guy, K Piper, J Sanders, P T Emmerson, C R Harwood
The dnaB-pheA (256 degrees-240 degrees) region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome containing genes responsible for stress responses, the utilization of plant cell walls and primary metabolism.
Microbiology (Reading): 1996, 142 ( Pt 11);3067-78
[PubMed:8969504]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)