Difference between revisions of "PhoR"
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
* '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P23545 P23545] | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P23545 P23545] | ||
| − | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu | + | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu:BSU29100] |
* '''E.C. number:''' | * '''E.C. number:''' | ||
Revision as of 03:42, 25 June 2009
- Description: two-component sensor kinase, regulation of phosphate metabolism
| Gene name | phoR |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase (OmpR family) |
| Function | regulation of phosphate metabolism |
| MW, pI | 64 kDa, 5.957 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1737 bp, 579 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | polA, phoP |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 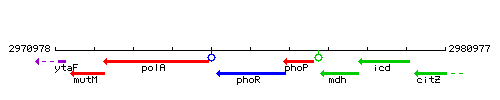
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29100
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: two transmembrane segments, C-terminal histidine phosphotransferase domain
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure: 3CWF
- Swiss prot entry: P23545
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Marion Hulett, University of Illinois at Chicago, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Amr Eldakak, F Marion Hulett
Cys303 in the histidine kinase PhoR is crucial for the phosphotransfer reaction in the PhoPR two-component system in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(2);410-21
[PubMed:17085571]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Salbi Paul, Stephanie Birkey, Wei Liu, F Marion Hulett
Autoinduction of Bacillus subtilis phoPR operon transcription results from enhanced transcription from EsigmaA- and EsigmaE-responsive promoters by phosphorylated PhoP.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(13);4262-75
[PubMed:15205429]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Zoltán Prágai, Nicholas E E Allenby, Nicola O'Connor, Sarah Dubrac, Georges Rapoport, Tarek Msadek, Colin R Harwood
Transcriptional regulation of the phoPR operon in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(4);1182-90
[PubMed:14762014]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Antelmann, C Scharf, M Hecker
Phosphate starvation-inducible proteins of Bacillus subtilis: proteomics and transcriptional analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(16);4478-90
[PubMed:10913081]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Shi, W Liu, F M Hulett
Decay of activated Bacillus subtilis pho response regulator, PhoP approximately P, involves the PhoR approximately P intermediate.
Biochemistry: 1999, 38(31);10119-25
[PubMed:10433720]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Shi, F M Hulett
The cytoplasmic kinase domain of PhoR is sufficient for the low phosphate-inducible expression of pho regulon genes in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 31(1);211-22
[PubMed:9987123]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jörg P Müler, Zhidong An, Tarek Merad, Ian C Hancock, Colin R Harwood
Influence of Bacillus subtilis phoR on cell wall anionic polymers.
Microbiology (Reading): 1997, 143 ( Pt 3);947-956
[PubMed:9084179]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)