Difference between revisions of "Pgk"
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
* essential {{PubMed|12682299}}, non-essential according to {{PubMed|23420519}} | * essential {{PubMed|12682299}}, non-essential according to {{PubMed|23420519}} | ||
| + | * suppression of ''[[ftsZ]]''(ts) mutation (reverted by addition of pyruvate) {{PubMed|24825009}} | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| Line 161: | Line 162: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed> 16479537, 12850135 , 17726680, 11489127 ,17505547 , 17218307 7154941 12682299 23420519 15378759</pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 16479537, 12850135 , 17726680, 11489127 ,17505547 , 17218307 7154941 12682299 23420519 15378759 24825009</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 17:14, 16 May 2014
- Description: phosphoglycerate kinase, glycolytic/ gluconeogenic enzyme, universally conserved protein
| Gene name | pgk |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | No |
| Product | phosphoglycerate kinase |
| Function | enzyme in glycolysis/ gluconeogenesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: pgk | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: pgk | |
| MW, pI | 42,0 kDa, 4.77 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1182 bp, 394 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | tpi, gapA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 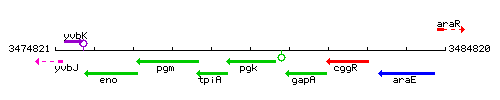
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
ATP synthesis, carbon core metabolism, phosphoproteins, universally conserved proteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU33930
Phenotypes of a mutant
- essential PubMed, non-essential according to PubMed
- suppression of ftsZ(ts) mutation (reverted by addition of pyruvate) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU33930
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + 3-phospho-D-glycerate = ADP + 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: phosphoglycerate kinase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: Two Substrate Reversible Michaelis-Menten PubMed
- Domains:
- nucleotide binding domain (ATP) (350–353)
- 2x substrate binding domain (21–23), (59–62)
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Inhibited by Co2+, NDP and NMP PubMed
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot), Cytoplasm (Homogeneous) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU33930
- Structure: 1PHP (from Geobacillus stearothermophilus)
- UniProt: P40924
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.2.3
Additional information
- extensive information on the structure and enzymatic properties of Pgk can be found at Proteopedia
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 12006 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 10462 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 5859 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2120 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2593 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP699 (pgk::cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab, PubMedlab
- GP707 (pgk::erm), available in Jörg Stülke's lab, PubMed
- Expression vector:
- pGP1102 (N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- pGP95 (N-terminal Strep-tag, in pGP172), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- pGP91 (N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, expression in B. subtilis, in pGP380), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- pGP1513 (expression in B. subtilis, in pBQ200), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion: pGP514 (in pAC6), a series of promoter deletion variants is also available in pAC6, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available iin Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References