Difference between revisions of "PGP172"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''Applications:''' | '''Applications:''' | ||
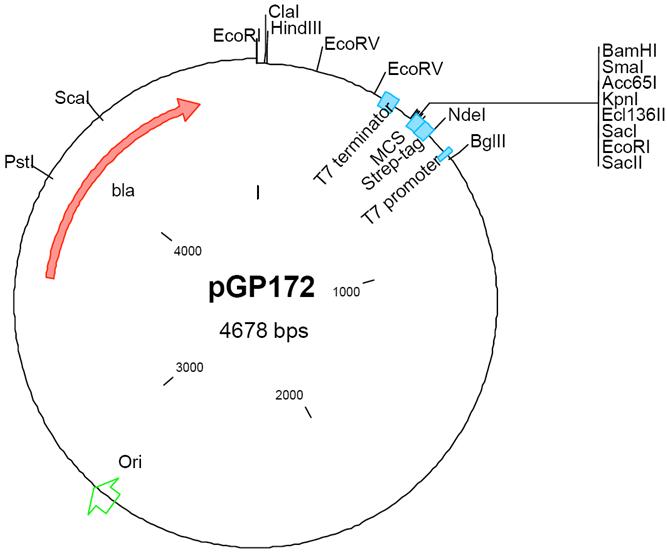
| − | Vector pGP172 was designed for the expression of proteins in ''E. coli'', the [[plasmid]] allows to fuse a Strep-tag to the N-terminus of the expressed protein. The ''E. coli'' strain BL21(DE3)/pLysS serves as a host strain and the expression of the desired protein is induced by the addition of 1 mM IPTG to the culture. pGP172 confers resistance to ampicillin in ''E. coli''. The plasmid was constructed in the [[Stülke]] lab and it is based on the vector pET3C. pGP172 is similar [[plasmid]] | + | Vector pGP172 was designed for the expression of proteins in ''E. coli'', the [[plasmid]] allows to fuse a Strep-tag to the N-terminus of the expressed protein. The ''E. coli'' strain BL21(DE3)/pLysS serves as a host strain and the expression of the desired protein is induced by the addition of 1 mM IPTG to the culture. pGP172 confers resistance to ampicillin in ''E. coli''. The plasmid was constructed in the [[Stülke]] lab and it is based on the vector pET3C. pGP172 is similar to [[plasmid]] [[pGP574]]. |
Sequencing primers: | Sequencing primers: | ||
Revision as of 15:58, 25 February 2010
Applications:
Vector pGP172 was designed for the expression of proteins in E. coli, the plasmid allows to fuse a Strep-tag to the N-terminus of the expressed protein. The E. coli strain BL21(DE3)/pLysS serves as a host strain and the expression of the desired protein is induced by the addition of 1 mM IPTG to the culture. pGP172 confers resistance to ampicillin in E. coli. The plasmid was constructed in the Stülke lab and it is based on the vector pET3C. pGP172 is similar to plasmid pGP574.
Sequencing primers:
- CD13: 5’-AAACATATGGCTAGCTGGAGCCACCCGCAGTTC -3’
- NP20: 5’-GCAGCAGCCAACTCAGCTTCCTTTCGGGC-3’
Matthias Merzbacher, Christian Detsch, Wolfgang Hillen, Jörg Stülke
Mycoplasma pneumoniae HPr kinase/phosphorylase.
Eur J Biochem: 2004, 271(2);367-74
[PubMed:14717704]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)