Difference between revisions of "NrgB"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | <pubmed>17001076 , 14600241 ,8282685 ,1670935 </pubmed> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
# Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | # Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 06:50, 31 May 2009
- Description: nitrogen-regulated PII-like protein
| Gene name | nrgB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | nitrogen-regulated PII-like protein |
| Function | regulation of ammonium uptake |
| MW, pI | 12 kDa, 8.825 |
| Gene length, protein length | 348 bp, 116 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | nrgA, bcrC |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 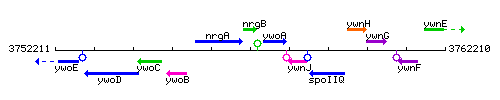
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates:
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: P(II) protein family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot), membrane
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: Q07428
- KEGG entry: BSU36520
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: induced by ammonium limitation
- Regulatory mechanism: transcription activation by TnrA
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody: available in Jörg Stülke lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Susan Fisher, Boston, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Annette Heinrich, Kathrin Woyda, Katja Brauburger, Gregor Meiss, Christian Detsch, Jörg Stülke, Karl Forchhammer
Interaction of the membrane-bound GlnK-AmtB complex with the master regulator of nitrogen metabolism TnrA in Bacillus subtilis.
J Biol Chem: 2006, 281(46);34909-17
[PubMed:17001076]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christian Detsch, Jörg Stülke
Ammonium utilization in Bacillus subtilis: transport and regulatory functions of NrgA and NrgB.
Microbiology (Reading): 2003, 149(Pt 11);3289-3297
[PubMed:14600241]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L V Wray, M R Atkinson, S H Fisher
The nitrogen-regulated Bacillus subtilis nrgAB operon encodes a membrane protein and a protein highly similar to the Escherichia coli glnB-encoded PII protein.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(1);108-14
[PubMed:8282685]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M R Atkinson, S H Fisher
Identification of genes and gene products whose expression is activated during nitrogen-limited growth in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1991, 173(1);23-7
[PubMed:1670935]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed