Difference between revisions of "Ndh"
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
** belongs to the 100 [[most abundant proteins]] {{PubMed|15378759}} | ** belongs to the 100 [[most abundant proteins]] {{PubMed|15378759}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3813 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 17593 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
Revision as of 09:50, 17 April 2014
- Description: NADH dehydrogenase (Menaquinone 7 & no proton)
| Gene name | ndh |
| Synonyms | yjlD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | NADH dehydrogenase (Menaquinone 7 & no proton) |
| Function | respiration |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ndh | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: Ndh | |
| MW, pI | 41 kDa, 6.289 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1176 bp, 392 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yjlC, uxaC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 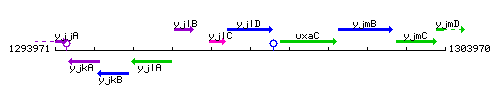
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed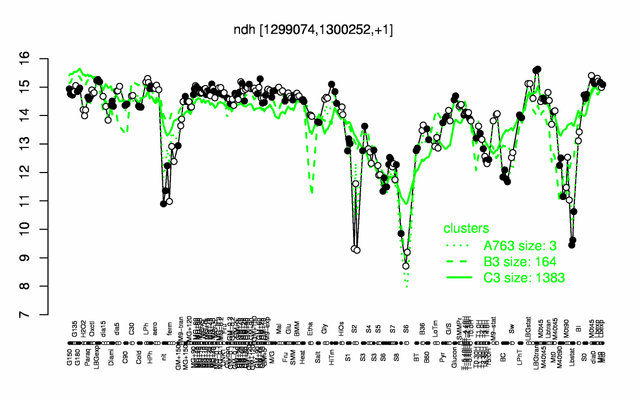
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
respiration, membrane proteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
Rex regulon, stringent response
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU12290
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU12290
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: NADH dehydrogenase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: membrane associated PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU12290
- Structure:
- UniProt: P80861
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3813 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 17593 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Frederik M Meyer, Jan Gerwig, Elke Hammer, Christina Herzberg, Fabian M Commichau, Uwe Völker, Jörg Stülke
Physical interactions between tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for a metabolon.
Metab Eng: 2011, 13(1);18-27
[PubMed:20933603]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Smita Gyan, Yoshihiko Shiohira, Ichiro Sato, Michio Takeuchi, Tsutomu Sato
Regulatory loop between redox sensing of the NADH/NAD(+) ratio by Rex (YdiH) and oxidation of NADH by NADH dehydrogenase Ndh in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(20);7062-71
[PubMed:17015645]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Michael Hecker
Bacillus subtilis functional genomics: global characterization of the stringent response by proteome and transcriptome analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(9);2500-20
[PubMed:11948165]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)