MreB
- Description: cell shape-determining protein, forms filaments, the polymers control/restrict the mobility of the cell wall elongation enzyme complex
| Gene name | mreB |
| Synonyms | divIVB |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | cell shape-determining protein |
| Function | cell shape determination |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mreB | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: MreB | |
| MW, pI | 35 kDa, 4.901 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1011 bp, 337 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mreC, radC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA Advanced_DNA |
Genetic context 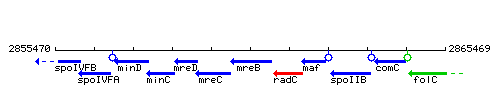
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell shape, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28030
Phenotypes of a mutant
- essential PubMed
- the mutation can be suppressed by inactivation of ponA, ptsI, ccpA PubMed, by overexpression of YvcK PubMed, or by addition of 5 mM magnesium to the growth medium PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ftsA/mreB family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- during logarithmic growth, MreB forms discrete patches thst move processively along peripheral tracks perpendicular to the cell axis PubMed
- forms transverse bands as cells enter the stationary phase PubMed
- close to the inner surface of the cytoplasmic membrane PubMed
- reports on helical structures formed by MreB PubMed seem to be misinterpretation of data PubMed
- normal localization depends on the presence of glucolipids, MreB forms irregular clusters in an ugtP mutant PubMed
Database entries
- UniProt: Q01465
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in the labs of Jeff Errington and Boris Görke
- Antibody: available in the Jeff Errington and Peter Graumann labs
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jeff Errington, Newcastle University, UK homepage
Peter Graumann, Freiburg University, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Additional reviews: PubMed
Arnaud Chastanet, Rut Carballido-Lopez
The actin-like MreB proteins in Bacillus subtilis: a new turn.
Front Biosci (Schol Ed): 2012, 4(4);1582-606
[PubMed:22652894]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Sven van Teeffelen, Zemer Gitai
Rotate into shape: MreB and bacterial morphogenesis.
EMBO J: 2011, 30(24);4856-7
[PubMed:22166997]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Courtney L White, James W Gober
MreB: pilot or passenger of cell wall synthesis?
Trends Microbiol: 2012, 20(2);74-9
[PubMed:22154164]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Andrew Jermy
Bacterial physiology: MreB takes a back seat.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2011, 9(8);560-1
[PubMed:21725336]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Matthew T Cabeen, Christine Jacobs-Wagner
The bacterial cytoskeleton.
Annu Rev Genet: 2010, 44;365-92
[PubMed:21047262]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kevin D Young
Bacterial shape: two-dimensional questions and possibilities.
Annu Rev Microbiol: 2010, 64;223-40
[PubMed:20825347]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Peter L Graumann
Cytoskeletal elements in bacteria.
Annu Rev Microbiol: 2007, 61;589-618
[PubMed:17506674]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Rut Carballido-López
The bacterial actin-like cytoskeleton.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2006, 70(4);888-909
[PubMed:17158703]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Linda A Amos, Fusinita van den Ent, Jan Löwe
Structural/functional homology between the bacterial and eukaryotic cytoskeletons.
Curr Opin Cell Biol: 2004, 16(1);24-31
[PubMed:15037301]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Localization
Felix Dempwolff, Christian Reimold, Michael Reth, Peter L Graumann
Bacillus subtilis MreB orthologs self-organize into filamentous structures underneath the cell membrane in a heterologous cell system.
PLoS One: 2011, 6(11);e27035
[PubMed:22069484]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ethan C Garner, Remi Bernard, Wenqin Wang, Xiaowei Zhuang, David Z Rudner, Tim Mitchison
Coupled, circumferential motions of the cell wall synthesis machinery and MreB filaments in B. subtilis.
Science: 2011, 333(6039);222-5
[PubMed:21636745]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Julia Domínguez-Escobar, Arnaud Chastanet, Alvaro H Crevenna, Vincent Fromion, Roland Wedlich-Söldner, Rut Carballido-López
Processive movement of MreB-associated cell wall biosynthetic complexes in bacteria.
Science: 2011, 333(6039);225-8
[PubMed:21636744]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Henrik Strahl, Leendert W Hamoen
Membrane potential is important for bacterial cell division.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2010, 107(27);12281-6
[PubMed:20566861]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hervé Joël Defeu Soufo, Peter L Graumann
Dynamic localization and interaction with other Bacillus subtilis actin-like proteins are important for the function of MreB.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 62(5);1340-56
[PubMed:17064365]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Other original publications
Additional publications: PubMed