Difference between revisions of "ImmR"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' transcriptional repressor, controls expression of genes of the mobile genetic element ICEBs1, induction by the SOS response or the [[RapI]]-[[PhrI]] sensory system <br/><br/> | + | * '''Description:''' transcriptional repressor ([[transcription factors of the Xre family|Xre family]]), controls expression of genes of the mobile genetic element ICEBs1, induction by the SOS response or the [[RapI]]-[[PhrI]] sensory system <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || transcriptional | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || transcriptional repressor ([[transcription factors of the Xre family|Xre family]]) |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || control of transfer of the mobile <br/>genetic element ICEBs1 | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || control of transfer of the mobile <br/>genetic element ICEBs1 | ||
Revision as of 16:54, 7 June 2014
- Description: transcriptional repressor (Xre family), controls expression of genes of the mobile genetic element ICEBs1, induction by the SOS response or the RapI-PhrI sensory system
| Gene name | immR |
| Synonyms | ydcN |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional repressor (Xre family) |
| Function | control of transfer of the mobile genetic element ICEBs1 |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: immR | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: ImmR | |
| MW, pI | 14 kDa, 4.989 |
| Gene length, protein length | 381 bp, 127 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | immA, xis |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 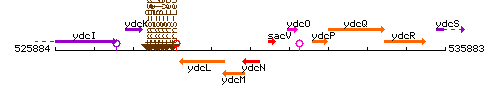
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, mobile genetic elements
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The ImmR regulon:
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU04820
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU04820
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity: binding of RapI to ImmR results in loss of DNA-binding activity of ImmR and subsequently in induction of ImmR-repressed genes PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU04820
- Structure:
- UniProt: P96631
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Baundauna Bose, Alan D Grossman
Regulation of horizontal gene transfer in Bacillus subtilis by activation of a conserved site-specific protease.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(1);22-9
[PubMed:21036995]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Baundauna Bose, Jennifer M Auchtung, Catherine A Lee, Alan D Grossman
A conserved anti-repressor controls horizontal gene transfer by proteolysis.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 70(3);570-82
[PubMed:18761623]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jennifer M Auchtung, Catherine A Lee, Katherine L Garrison, Alan D Grossman
Identification and characterization of the immunity repressor (ImmR) that controls the mobile genetic element ICEBs1 of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 64(6);1515-28
[PubMed:17511812]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)